Figure 4.
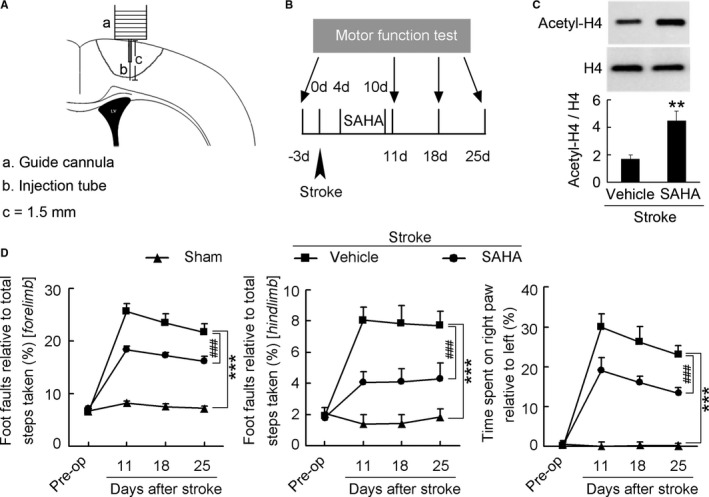
Delayed SAHA treatment promotes functional recovery from stroke. A, Diagram showing the microinjection of SAHA via an implanted microcannula into the peri‐infarct cortex of conscious mice. B, Diagram showing the design of the experiment (C and D). SAHA was microinjected into the peri‐infarct cortex of mice during 4 to 10 d after stroke. C, Immunoblots showing that SAHA significantly increased acetyl‐H4 level in the peri‐infarct cortex. SAHA (10 μmol/L) or vehicle was microinjected into the peri‐infarct cortex during 4 to 10 d (2 μL/d) and immunoblots were performed at 11 d after stroke. (n=4 for each group, 1‐way ANOVA, **P<0.01). D, Left: Foot faults of left forelimb in the grid‐walking task. Middle: Foot faults of left hindlimb in the grid‐walking task. Right: Forelimb symmetry in the cylinder task. (n=10, 13, and 13 for sham, vehicle, and SAHA, respectively, per time point, 2‐way ANOVA, ***P<0.001, vs sham; ### P<0.001, vs vehicle). SAHA indicates suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid.
