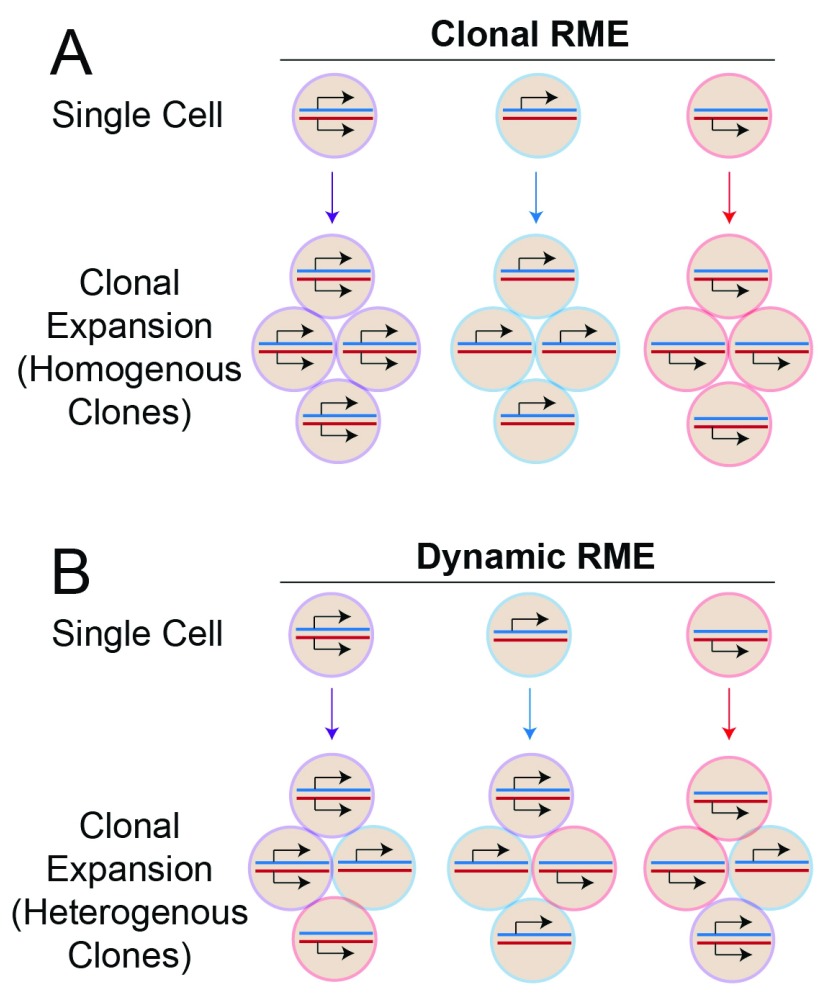
Figure 2. Schematic depiction of clonal versus dynamic random monoallelic expression (RME).
( A) Clonal RME is identified when a single cell is expanded to form a colony of daughter cells and each daughter cell has the same allele expression pattern as the original parent cell. Typically, studies of this phenomenon use cell lines and expand them clonally and then profile allelic expression from the entire batch of cells in the clone. They find that some clones exclusively express one allele, others are biallelic, and others express only the other allele (homogenous clones). ( B) Dynamic RME occurs when a single cell is expanded to form a colony but the individual cells in the colony have different allelic expression patterns (heterogeneous clones). This phenomenon is detectable only by using single-cell transcriptome analysis and cannot be identified from profiles of the whole batch of cells in the clone, as was done in previous cell line studies reporting widespread clonal RME.