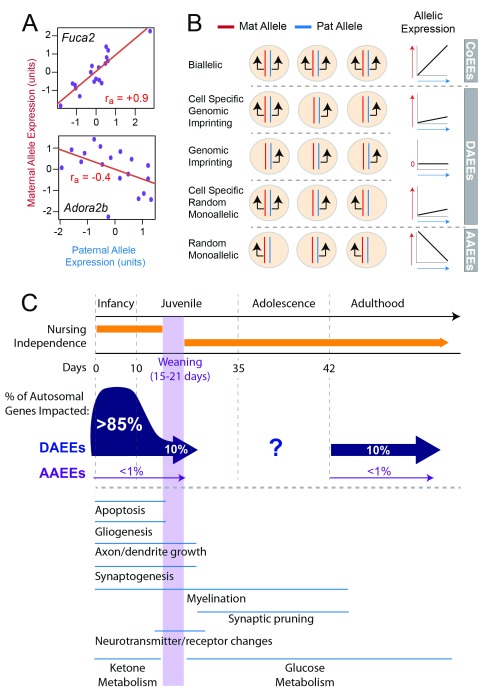
Figure 3. RNA-Seq approach to screen for high-confidence, non-genetic differential allele expression effects in vivo.
( A) The approach involves RNA-Seq profiling of maternal and paternal allele expression levels across a population of individuals and examining the correlated expression of the two alleles across the population. For example, Fuca2 exhibits highly correlated allelic expression, while the maternal and paternal alleles for Adora2b are negatively correlated. Statistical modeling is performed to estimate the effects of technical noise, biological variation, and genetic variation on the data. The resulting statistic identifies high-confidence, non-genetic allelic effects in a genome-wide manner for any tissue. ( B) This in vivo screening approach can detect diverse forms of allelic effects. Biallelic expression at the cellular level is expected to manifest as highly correlated allelic expression. Clonal random monoallelic expression (RME) that is similar to X-inactivation will manifest as a negative allele correlation (antagonistic allele expression effects, or AAEEs), since more maternal allele-expressing cells arise at the expense of paternal allele-expressing cells and vice versa. Genome imprinting and cell-specific imprinting or RME will manifest as a weak correlation or no correlation between the alleles; we refer to these cases more generally as differential allele expression effects (DAEEs). ( C) Profiling of non-genetic allelic effects in the postnatal day 5 (P5) and P15 and adult mouse DRN revealed major developmental differences. Most genes exhibit evidence for high-confidence DAEEs in the P5 DRN, but these effects are reduced by P15 and in adults such that only 10% of autosomal genes exhibit DAEEs at these older ages. AAEEs are rare in vivo and impact less than 1% of all autosomal genes expressed. The in vivo developmental shift in non-genetic allelic effects is presented relative to other major developmental milestones and processes in the mouse brain. We applied a similar approach to study DAEEs in the primate brain. CoEE, co-expression effect.