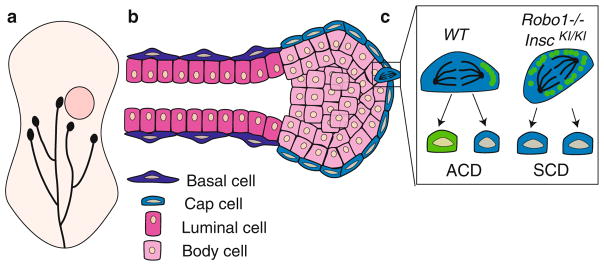
Fig. 16.6.
SLIT2/ROBO1 signaling in the mammary gland. (a) Cartoon of developing mammary gland. Mammary ducts (black) grow postnatally from the nipple into the fat pad (beige) and at 5.5 weeks reach the lymph node (pink circle). Capping each duct is a terminal end bud, which serves as a site of cell proliferation. (b) Longitudinal section through a terminal end bud and subtending duct. Each duct is bilayered with an outer layer of basal cells and an inner layer of luminal cells. The terminal end bud is a spherical structure with an outer layer of cap cells and inner layers of luminal body cells. (c) SLIT2/ROBO1 signaling in the cap cells of the terminal end bud regulates cell division. In a WT terminal end bud, cap cells undergo ACD and are renewed (blue) while generating a progenitor cell (green). This is due to the expression of INSC (green circles) that accumulates on one side of the dividing cell. Loss of Robo1 (Robo1−/−) or overexpression of Insc (InscKI/KI), both of which increase INSC levels in the cell, results in a switch in division mode from ACD to SCD