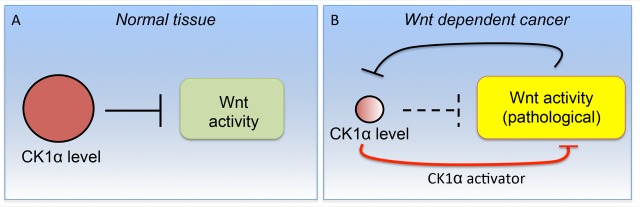
Figure 1. A schematic suggesting the mechanism underlying the enhanced therapeutic index observed with SSTC3.
A. In normal tissue, constitutive CK1α levels are sufficient to maintain Wnt signaling at relatively low levels. B. In Wnt-dependent cancer cells, hyperactivated Wnt activity acts to suppress CK1α levels via an unknown mechanism. These reduced levels of CK1α result in its activity becoming rate limiting in Wnt-dependent tumors. In this context, pharmacological CK1α activators compensate for the insufficiency of CK1α activity, resulting in suppression of Wnt activity.