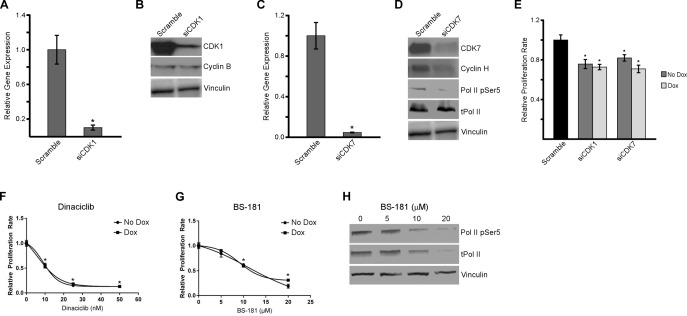
Figure 6. Inhibition of CDK1 and CDK7 decreases proliferation of TNBC cells.
siRNA-mediated knockdown of CDK1 A. and B. and CDK7 C. and D. in MDA-MB-231-ERβ cells were verified at both the mRNA and protein level. The impact of CDK1 (B) and CDK7 (D) knockdown on the protein expression levels of their respective binding partners, cyclin B and cyclin H, as well as RNA Polymerase II phospho-serine 5 for siCDK7 treated cells, are shown. Total RNA Polymerase II and Vinculin are shown as loading controls. E. Proliferation rates of MDA-MB-231-ERβ cells six days after siRNA mediated knockdown of CDK1 and CDK7 in the absence (No Dox) and presence (Dox) of ERβ expression relative to scrambled siRNA control transfected cells. Dose response curves indicating the effects of dinaciclib F., a CDK1 inhibitor, and BS-181 G., a CDK7 inhibitor, on the proliferation rates of MDA-MB-231-ERβ cells in the presence and absence of ERβ expression after six days of treatment. The effects of four hours of drug mediated inhibition of CDK7 on the protein levels of total RNA polymerase II and RNA polymerase II phospho-serine 5 were also examined H. Vinculin is shown as a loading control. * Denotes significance at the P ≤ 0.05 level compared to controls.