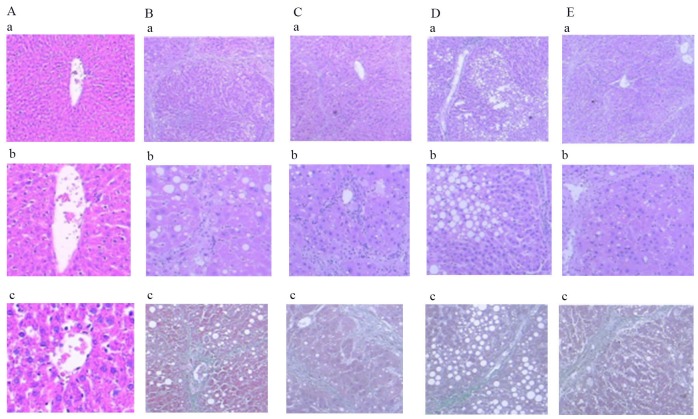
Figure 7. Comparison of HE and Masson staining in liver of rats in each group.
(a-1) Normal group: HE staining, ×40, normal hepatic cell morphology. (b-1) Modal group: HE staining, ×40, disruption of structure of hepatic lobules, false leaflet formation. (c-1) Treatment group: HE staining, ×40, the collagen fibers are linked to each other, and are wrapped around the liver. (d-1) Intervention group: HE staining, ×40, Collagen fibers extend and are not connected to each other. (e-1) Natural recovery group: HE staining, ×40, Collagen fibers extend and connect with each other. (a-2) Normal group: HE staining, ×100, normal hepatic cell morphology. (b-2) Modal group: HE staining, ×100, disruption of structure of hepatic lobules. (c-2) Treatment group: HE staining, ×100, complete destruction of hepatic leaflet structure. (d-2) Intervention group: HE staining, ×100, Collagen fibers to mild periportal extension. (e-2) Natural recovery group: HE staining, ×100, Collagen fibers extend significantly. (a-3) Normal group: Masson staining, ×200, normal hepatic cell morphology. (b-3) Modal group: Masson staining, ×100, fiber hyperplasia. (c-3) Treatment group: Masson staining, ×100, structural disorder of hepatic lobe. (d-3) Intervention group: Masson staining, ×100, Collagen fibers extend outward from the central veins. (e-3) Natural recovery group: Masson staining, ×100, Collagen fibers extend outward.