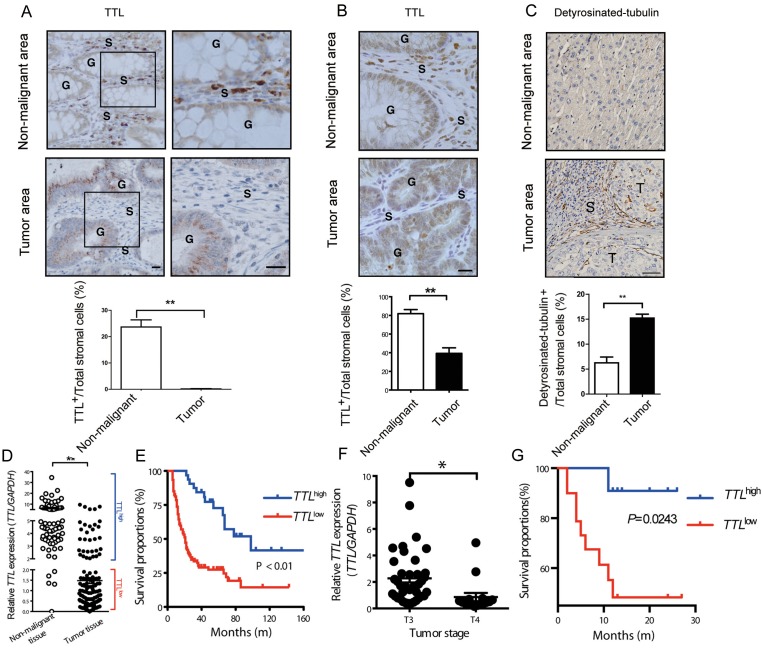
Figure 5. Suppressed TTL expression in stromal cells of human colon and liver cancer tissues.
(A) Paraffin-embedded tissue samples ± 1 cm from the boundary of a tumor nodule (tumor area) or more than 2 cm away from tumor nodules (non-malignant areas) of human colon carcinoma were stained by immunohistochemistry for TTL (brown). (Upper left panel) Representative images from colon areas of one patient; boxed areas enlarged next to original (upper right panel); G, colonic glands; S, stroma; scale bars, 20 μm. (B) Representative images of TTL+ cells (brown) stained in non-malignant and adenoma areas of the colon tissues from a mouse model of intestinal inflammation-induced carcinogenesis (AOM/DSS). G, colonic glands; S, stromal surrounding the colonic glands; scale bars, 20 μm. (C) Tumor and non-tumor areas as described in (A) from human hepatocarcinoma tissues were stained for detyrosinated-tubulin (abbreviated as “Glu-tublin”, brown). Representative images from liver tissue areas from one patient. T, tumor nests; S, stroma. Bars, 50 μm. (A-C, lower panels) Proportions of TTL+ or detyrosinated-tubulin+ stromal cells were calculated by counting TTL+ or detyrosinated-tubulin+ stromal cells and all nuclei within the stroma from 35 visual fields (AOM/DSS induced), or 6 visual fields (human colon or liver) tissue sample. Mean ± SEM, **P< 0.01, Student’s t test, n=6 tumors per group. (D) Human TTL mRNA levels in non-malignant colon tissues (n = 72) and colon tumor tissues (n = 77). Scatter plot and mean, **P < 0.0001, Student’s t test. Cut-off value for definition of TTLhigh samples set as 2.0. (E) TTLlow and TTLhigh expression in colon tumor tissue was correlated to the overall survival of the colon tumor patients after surgery. P < 0.01, log-rank test, n = 72. (F) The TTL expression levels in colon tumor tissues from T3 (n = 42) and T4 stage (n = 16) were compared. Scatter plot and mean, *P= 0.012, Student’s t test. (G) TTLlow and TTLhigh expression in liver tumor tissues was defined as described in (D) and correlated to the overall survival times of the hepatocarcinoma patients after surgery. P= 0.0243, log-rank test, n = 31.