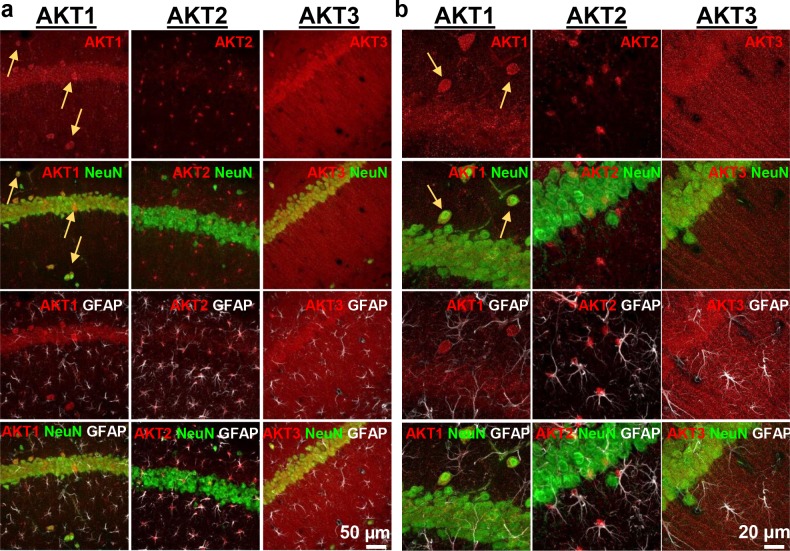
Figure 2. Cell-type-specific expression of AKT isoforms in hippocampal area CA1.
(a). AKT1 was mainly expressed in neuronal cell bodies, indicated by co-localization with NeuN. Certain neurons in the pyramidal layer, stratum oriens and molecular layer showed greater expression levels of AKT1 (yellow arrows). AKT2 was specifically expressed in astrocytes, shown by co-localization with the astrocyte marker GFAP. AKT3 co-localized with NeuN like AKT1 but was also expressed in the stratum radiatum, most likely within dendrites. (b) Higher magnification showed no specific co-localization of AKT1 with GFAP and that certain neurons in the stratum oriens expressed high levels of AKT1 (yellow arrows). AKT2 was mainly expressed in the cell bodies of astrocytes. AKT3 showed high expression levels in neuronal cell bodies and dendrites and some expression in astrocytes.