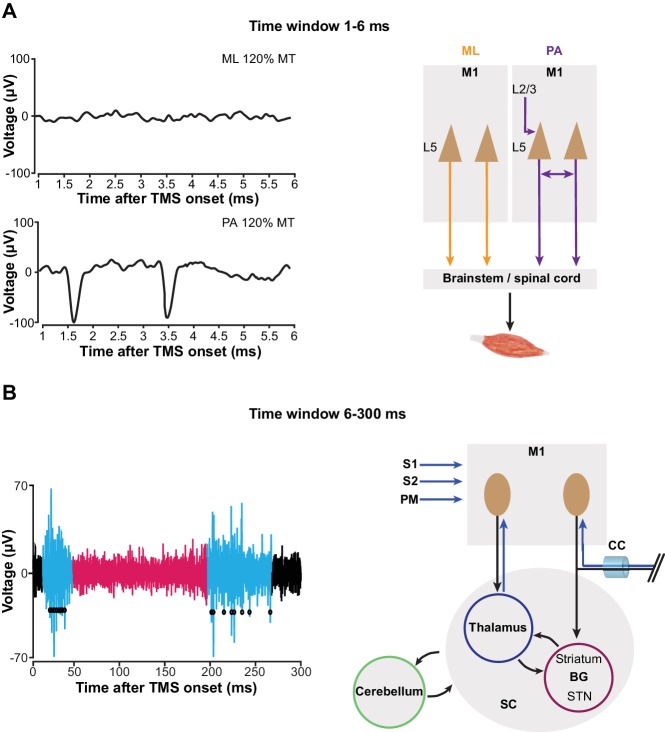
Figure 9. mspTMS activates different neuronal circuits depending on stimulus orientation or the time-window of investigation.
(A) In the short-latency time window (1–6 ms after onset), ML- and PA-oriented mspTMS evoked different patterns of neuronal activities in layer V of CFA (left panel). ML stimuli activated the descending PT pathways, while PA stimuli triggered an oscillatory spiking event that reflects the local connectivity within M1 (right panel). (B) In the long-latency time window (6–300 ms after onset), mspTMS evoked a multiphasic response alternating between excitation and inhibition (left panel shows a raw spike trace evoked by a suprathreshold stimulus; blue and red code for phase of significant excitation and inhibition, respectively, adopted from Figure 7). This multiphasic pattern is generated through multiple possible long-range circuits activated by mspTMS (right panel). Abbreviations: BG, basal ganglia; CC, corpus callosum; M1, primary motor cortex; PM, premotor cortex; S1/S2, somatosensory cortices; SC, subcortical structures; STN, subthalamic nucleus.