Figure 2.
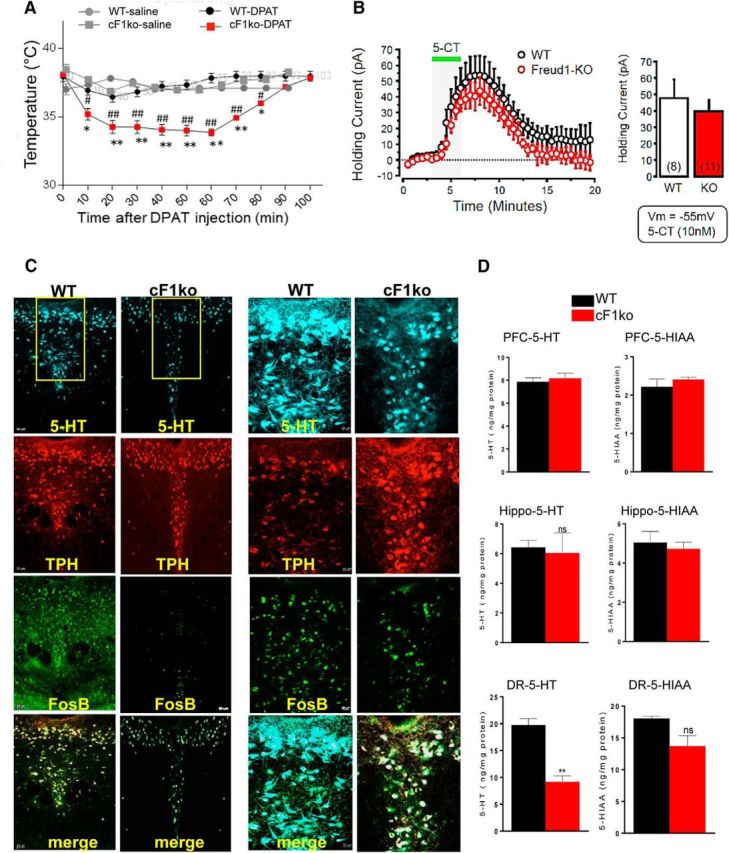
Loss of Freud-1 augments 5-HT1A autoreceptor function and reduces 5-HT neuron activity and 5-HT levels. A, 5-HT1A-induced hypothermia. 8-OH-DPAT (0.75 mg/kg, i.p.) induced a greater body temperature reduction in cF1ko compared with F1wt (WT). Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3/group). *p < 0.05 versus WT-saline. **p < 0.001 versus WT-DPAT. #p < 0.05 versus cF1ko-saline. ##p < 0.001 versus cF1ko-DPAT. B, Whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings (Vm = −55 mV) of 5-HT neurons in slices of DR in vitro, from cF1ko or F1wt mice (n = 4) in response to 5-CT (10 nm). No significant difference in 5-HT1A receptor-induced outward current was observed. C, Reduced 5-HT- and FosB-stained cells in cF1ko raphe. DR sections of cF1ko or F1wt (WT) mice stained for 5-HT, TPH, and FosB shown at 10× (Scale bar: left, 50 μm) or 20× magnification of boxed region (Scale bar: right, 20 μm). D, Reduced raphe 5-HT content in cF1ko mice. Tissue 5-HT and 5-HIAA content was quantified by HPLC for DR, hippocampus (Hippo), and PFC of cF1ko versus WT mice. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3/group); reduced raphe 5-HT content in cF1ko versus WT mice (unpaired two-tailed Student's t test, df = 4, t = 6.675). **p < 0.01.
