Figure 4.
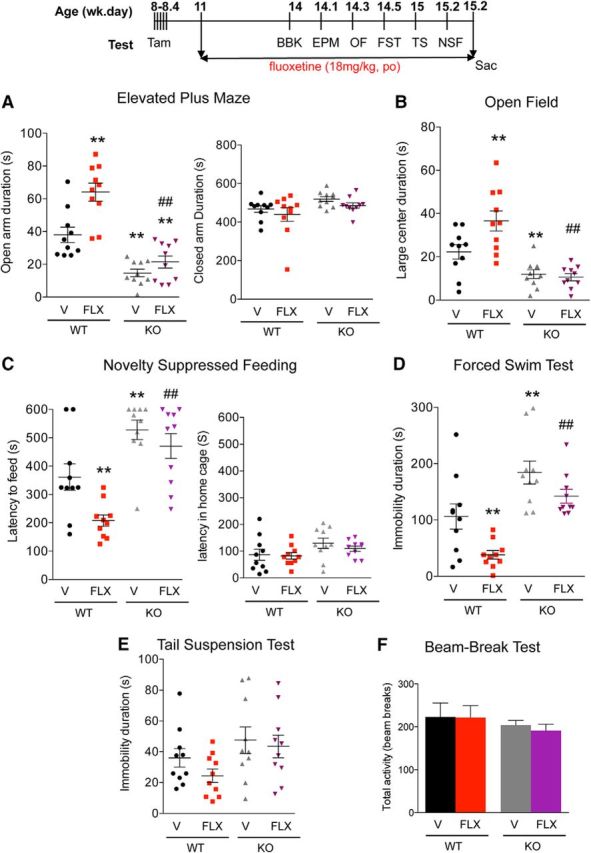
Resistance to chronic SSRI treatment in cF1ko mice. WT or cF1ko (KO) mice were treated with FLX or vehicle (V) for 3 weeks and throughout the behavioral assays (timeline). A–C, Anxiety phenotype: chronic FLX reduced anxiety in WT mice but did not affect the increased anxiety seen in cF1ko mice. A, EPM, significant changes in time spent in open arms in EPM test (one-way ANOVA treatment × genotype interaction, F(3,36) = 27.01, p < 0.01; post hoc Tukey). **p < 0.01 versus WT-V. ##p < 0.01 versus WT-FLX. B, OF, changes in distance traveled in large center (one-way ANOVA treatment × genotype interaction, F(3,36)) = 14.53, p < 0.01; post hoc Tukey). **p < 0.01 versus WT-V, ##p < 0.01 versus WT-FLX. C, NSF, latency to approach food in novel arena (one-way ANOVA treatment × genotype interaction, F(3,36) = 14.16, p < 0.01; post hoc Tukey). **p < 0.01 versus WT-V. ##p < 0.01 versus WT-FLX. D, E, Depression phenotype. D, FST. Depression-like behavior in cF1ko (V) compared with F1wt (V) was indicated by increased immobility in the FST. Chronic FLX significantly reduced immobility in F1wt, but not in cF1ko mice (one-way ANOVA treatment × genotype interaction, F(3,36) = 13.62, p < 0.01; post hoc Tukey). **p < 0.01 versus WT-V. ##p < 0.01 versus WT-FLX. E, TST, no significant changes were observed. F, BBK test. No differences in 30 min activity in novel arena were observed. Data represent individual animals with mean ± SEM; n = 10/group. **p < 0.01 versus WT-V. ##p < 0.01 versus WT-FLX.
