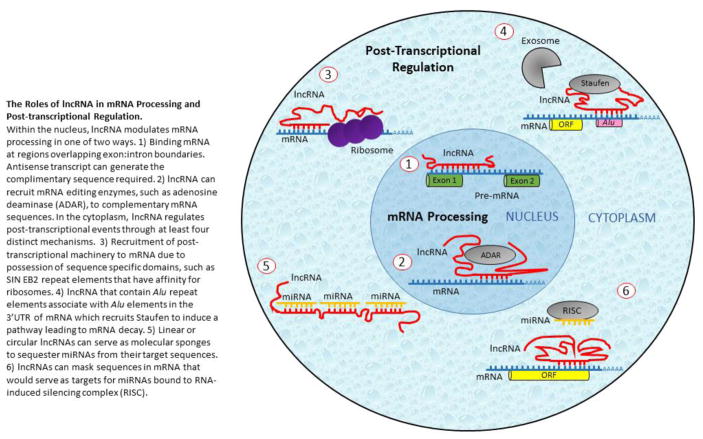
Figure 3. The Roles of lncRNA in mRNA Processing and Post-transcriptional Regulation.
Within the nucleus, lncRNA modulates mRNA processing in one of two ways. 1) Binding mRNA at regions overlapping exon:intron boundaries. Antisense transcript can generate the complimentary sequence required. 2) lncRNA can recruit mRNA editing enzymes, such as adenosine deaminase (ADAR), to complementary mRNA sequences. In the cytoplasm, lncRNA regulates post-transcriptional events through at least four distinct mechanisms. 3) Recruitment of post-transcriptional machinery to mRNA due to possession of sequence specific domains, such as SIN EB2 repeat elements that have affinity for ribosomes. 4) lncRNA that contain Alu repeat elements associate with Alu elements in the 3′UTR of mRNA which recruits Staufen to induce a pathway leading to mRNA decay. 5) Linear or circular lncRNAs can serve as molecular sponges to sequester miRNAs from their target sequences. 6) lncRNAs can mask sequences in mRNA that would serve as targets for miRNAs bound to RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC).