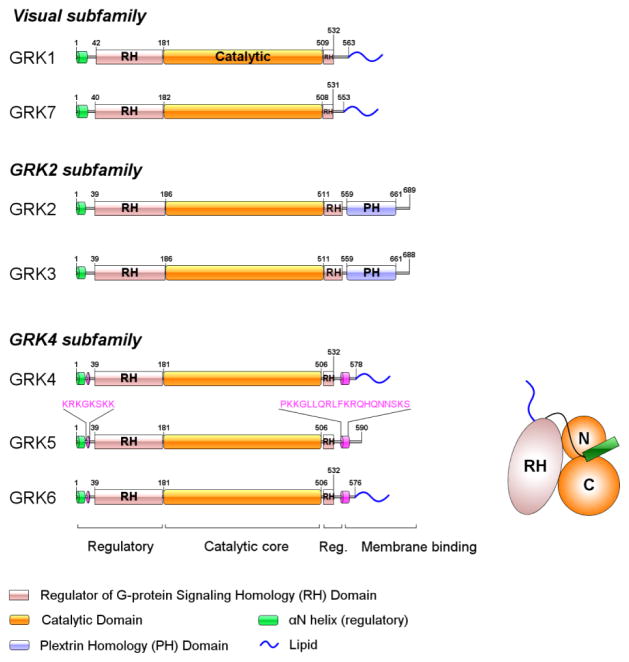
Figure 1. General architecture of GRKs.
GRKs are divided into 3 subfamilies based on sequence homology and are composed of two main domains, Regulator of G protein signaling Homology (RH) and catalytic domains. αN-helix comprising the first ~20 residues plays a regulatory role by bridging the N- and C-lobes of catalytic domain. The C-terminal fragment mediates membrane localization of GRKs. GRK4 subfamily includes two polybasic regions at N- and C-termini, and GRK5 relies on these regions to interact with negatively-charged phospholipids. GRK2 and GRK3 have a PH domain that interacts with acidic phospholipids and Gβγ subunits.