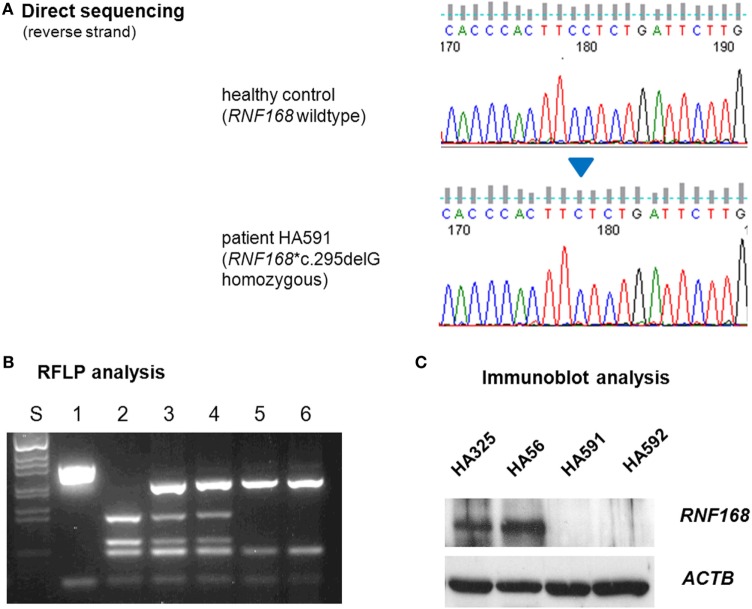
Figure 2.
Assessment of RNF168 mutation (A) and RNF168 protein level (B). (A) Direct sequencing of RNF168 exon 12 reveals homozygosity for the novel frameshift mutation c.295delG in genomic DNA from either of both patients (HA591, HA592). (B) RFLP analysis of PCR products on 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. S, size marker; 1, undigested PCR product; 2–6, PCR products cleaved with MnlI: 2, wild-type control, 3, paternal sample, 4. maternal sample, 5, patient HA591, 6, patient HA592. (C) Western blot analysis reveals strongly reduced immunoreactivity for RNF168 protein in lymphoblastoid cells from either of both patients (HA591, HA592). Lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) from a healthy individual were used as an RNF168-proficient control (HA325), and LCLs from a patient with classical ataxia–telangiectasia were used for comparison (HA56). β-actin served as the loading control (ACTB).