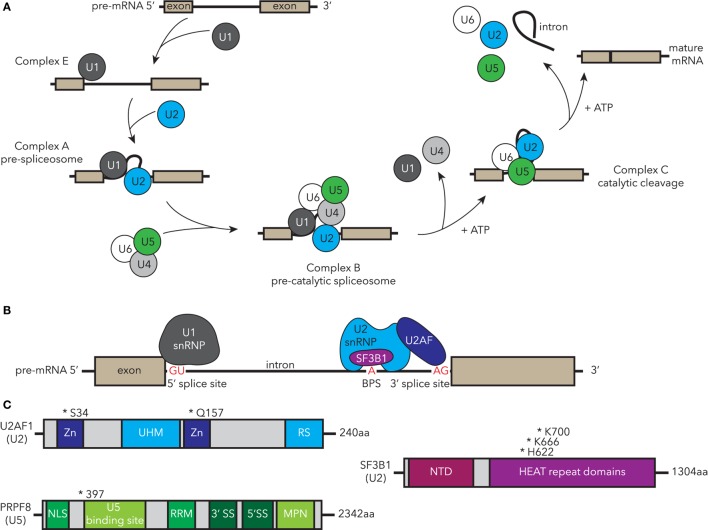
Figure 2.
Human MDS-associated mutations in essential components of the spliceosome are conserved in zebrafish disease models. (A) Spliceosomal processing of pre-mRNA to mature transcript, indicating recruitment of snRNP complexes. Complexes containing MDS-mutated factors that have been studied in zebrafish are highlighted in blue (U2) and green (U5). (B) Essential components of complex A, including binding of the U1 snRNP to the 5′ splice site (SS), and U2 snRNP U2AF recognition and binding of AG in the 3′ SS, while SF3B1 recognizes the branch point site (BPS). (C) Structure and common MDS-associated mutations in U2-associated components U2AF1 and SF3B1 and U5 PRPF8. Zn, zinc finger domain; UHM, U2AF homology motif; RS, arginine-serine domain; NTD, N-terminal domain; NLS, nuclear localization sequence; RRM, RNA recognition motif; MDS, myelodysplastic syndrome; snRNP, small nuclear ribonucleo-protein; U2AF1, U2 small auxiliary factor 1; SF3B1, splicing factor 3B, subunit 1; PRPF8, pre-mRNA processing factor 8.