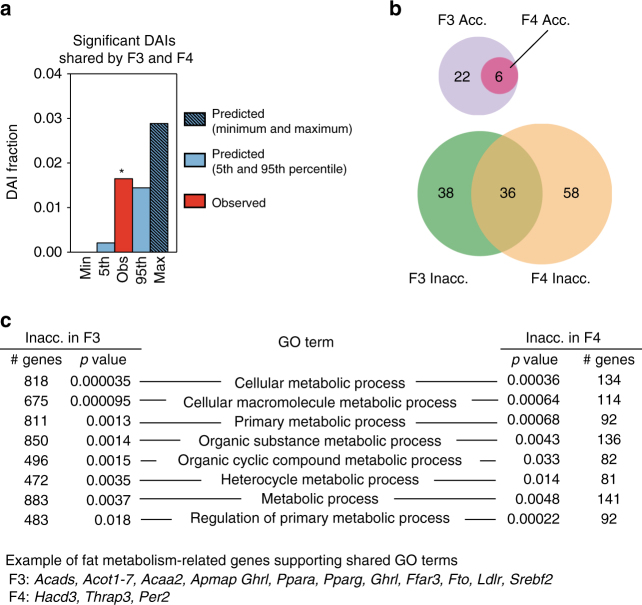
Fig. 6.
TBT-dependent changes in sperm chromatin accessibility preferentially relate with metabolic functions. Chromosomal regions with uniform base composition showing significant differential ATAC-seq read coverage or differentially accessible isochores (DAIs) were defined using MEDIPS (see Methods for further details). DAIs for which ATAC-seq read coverage was larger in TBT than in DMSO samples were deemed as accessible DAIs (Acc.), whereas DAIs for which ATAC-seq read coverage was larger in DMSO than in TBT samples were deemed as inaccessible DAIs (Inacc.). a The fraction of significant DAIs with the same direction of change both in F3 and F4 samples i.e., F3-F4 shared DAIs was larger than expected by chance. Data is presented as mean ± s.e.m. *p < 0.05. b Venn diagrams representing the overlap for GO terms enriched for genes spanned by significant DAIs for each generation separately. GRCm38/mm10 mouse reference genome sequence genes spanned by significant DAIs in the same direction for each generation separately were identified using the tool “Genomic Regions Search” from MouseMine61. Significant enrichment for GO terms were identified using MouseMine, the background population of annotations for mouse genome as reference set, and Benjamini Hochberg correction for multiple testing to calculate p values according to the hypergeometric distribution (threshold of significance p = 0.05)61. c List of selected GO terms enriched for genes within significantly inaccessible DAIs in both generations with direct ties to metabolic processes (see Supplementary Data 19 for full list)