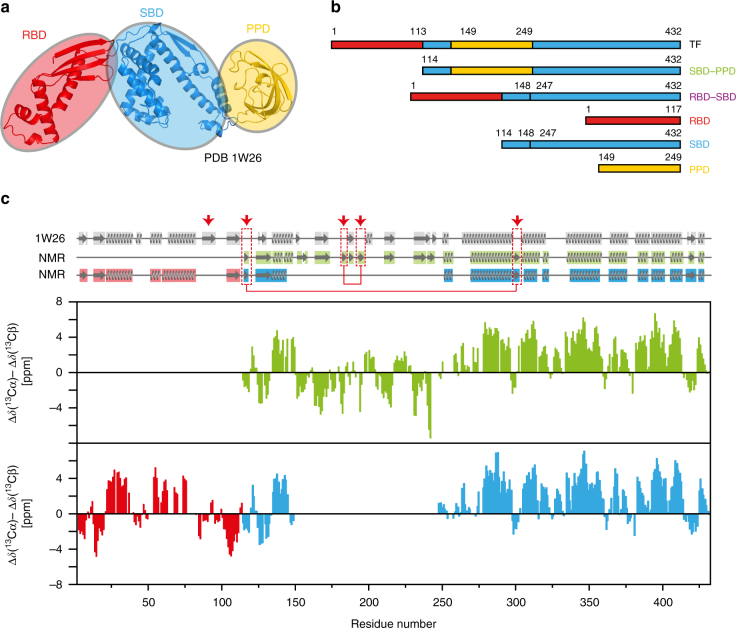
Fig. 1.
Domain organization of full-length TF and secondary structure elements in solution. a On the ribbon representation of a published TF crystal structure (PDB 1W268), the three domains ribosome-binding domain (RBD), substrate-binding domain (SBD), and peptidyl-prolyl-cis/trans isomerase domain (PPD) are colored in red, blue, and yellow, respectively. b Domain constructs of E. coli TF used in this work. Six constructs of TF domains are shown with amino acid numbering corresponding to full-length TF. The names define a color code used throughout this work. c Secondary 13C chemical shifts plotted against the amino acid residue number of TF, as determined from triple-resonance experiments in the domain constructs SBD–PPD (green), RBD (red), and SBD (blue). A 1–2–1 weighting function for residues (i−1)–i–(i + 1) has been applied to the raw data to reduce noise and highlight regular secondary structure elements. Secondary structure elements were calculated for the crystal structure (PDB 1W26, gray) with DSSP12 and for the NMR data with CSI 3.013 and are indicated on top. The red arrows and boxes highlight structural elements detected only in solution