Fig. 7.
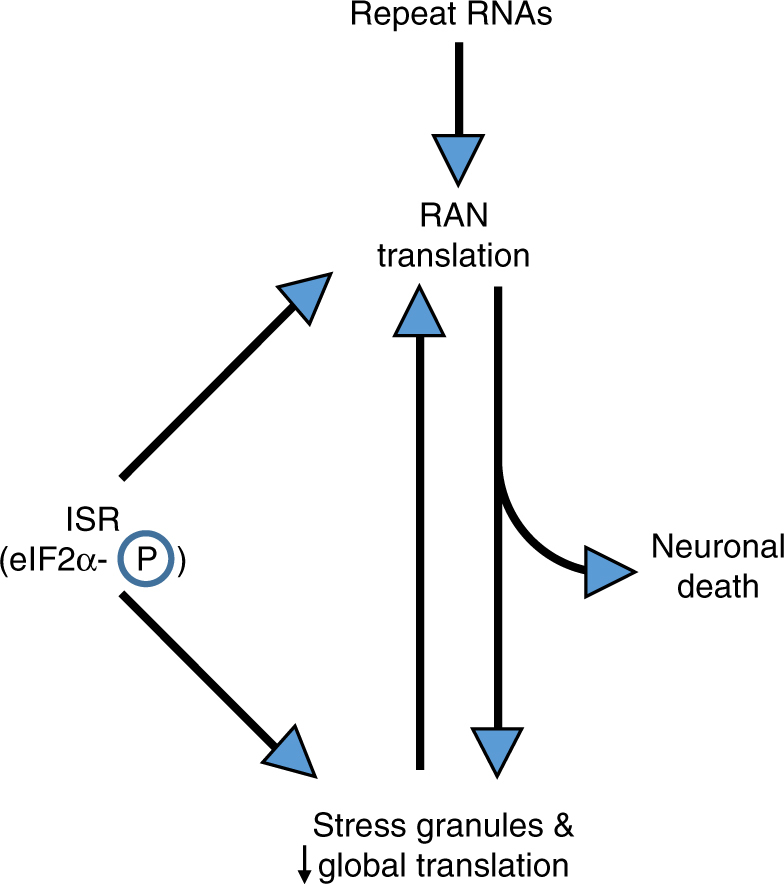
Working model for how a feed-forward loop activates RAN translation and cellular stress pathways. Repeat expansions trigger RAN translation. RAN proteins or the repeat RNAs themselves then elicit stress granules and suppress global protein synthesis in a phosphorylated-eIF2α-dependent manner. Activation of the integrated stress response (ISR) and phosphorylation of eIF2α, either by the repeat RNAs or RAN proteins directly or through exogenous cellular stress, can further trigger stress granule formation and suppress global translation while selectively enhancing RAN translation. This creates a feed-forward loop that can contribute to neuronal dysfunction and death
