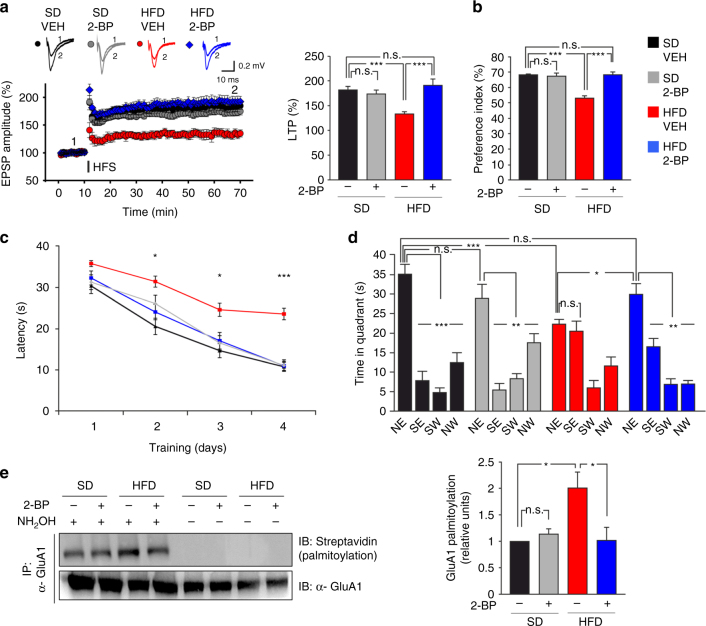
Fig. 6.
2-BP reverts GluA1 palmitoylation and rescues both synaptic plasticity impairment and memory loss induced by HFD. a Time course (left) of LTP at CA3-CA1 synapses induced by HFS delivered at time 10 (line) in hippocampal slices of mice fed with SD or HFD for 6 weeks and intranasally injected with vehicle or 2-BP (SDVEH, SD2-BP, HFDVEH, HFD2-BP; n = 12 slices per each group). Results are expressed as percentages of baseline EPSP amplitude (=100%). Insets (top) show representative EPSPs at baseline (1) and during the last 5 min of LTP recording (2). On right, LTP recorded during the last 5 min (statistics by two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc). b Preference for the novel object in NOR paradigm (n = 9 for each group; statistics by two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc). c Latency to reach the hidden platform in MWM test (n = 9 for each group; significance is indicated between SDVEH or HFD2-BP and HFDVEH mice; statistics by two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc). d Time spent in the four quadrants during probe test of MWM test. NE is the target quadrant (n = 9 for each group; statistics by two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc). e Immunoblots (left) of palmitoylated GluA1 (top) and total immunoprecipitated protein (bottom) in hippocampi of SD and HFD mice. On right, densitometry of palmitoylated GluA1/total immunoprecipitated GluA1 amount ratio (n = 4; statistics by two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; n.s. not significant. See also Supplementary Fig. 5