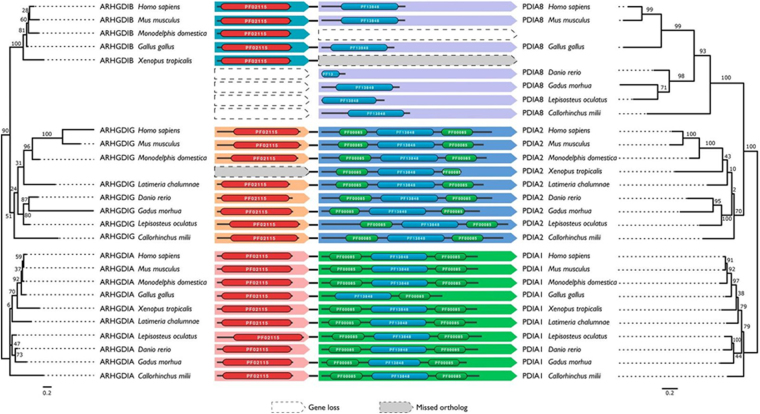
Figure 2.
Evolutionary histories of the PDI and RhoGDI paralogs, respectively, in the three human PDI/RhoGDI gene clusters. The trees are based on the maximum likelihood phylogeny of the PDIs and RhoGDIs, respectively, but were adapted for congruency with the species phylogeny. Topology testing revealed that the adapted topology is not significantly worse compared to the ML topology (SH test: p > 0.05). Branch labels denote percent bootstrap support. The Pfam83 domain architectures of the individual PDI and RhoGDI proteins are shown next to the leaf labels: PF02115 – Rho_GDI; PF13848 – Thioredoxin_6; PF00085 – Thioredoxin. The architectures are connected if the genes reside next to each other in the genome of the respective species. The orthologous groups, PDIA1, PDIA2, PDIA8 and correspondingly, RhoGDIα, RhoGDIγ and RhoGDIβ are indicated by the same background color. In two cases, an ortholog was not predicted, while gene order indicates its presence (‘missed ortholog’).