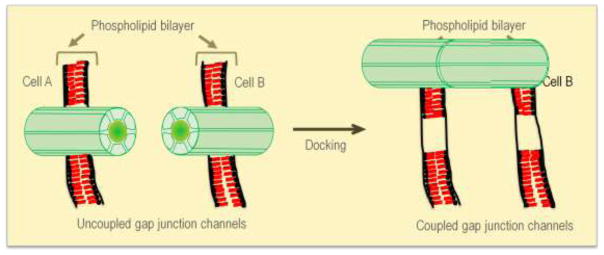
Figure 2. Docking of connexons leads to coupled junctions.
Gap junction intercellular communication is dependent on successful docking of two connexons located on two adjacent cells. When connexons present on the cell surface of one cell dock with connexons present on the cell surface of an adjacent cell it can lead to interlocking of the extracellular domains of each connexon allowing the formation of a gap junction connexin channel between two adjacent cells. These channels allow exchange of small molecules and ions permitting cell to cell communication.