Figure 1. Classification scheme and cellular localization of CFTR variants.
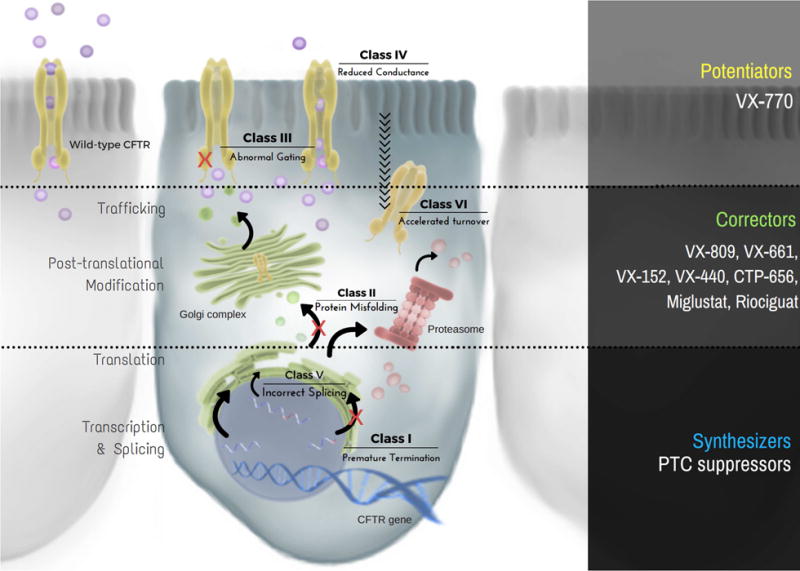
Class I and V defects result in diminished protein production, whereas class II and VI yield reduced stability of CFTR. In addition, class III and IV variants inhibit channel function or activity of cell surface associated CFTR. Molecular-based therapeutic strategies target each of these categories and include the following: (1) ‘synthesizers’, which rescue CFTR protein production (e.g. suppression of premature truncation codons, or PTCs), (2) ‘correctors’, which augment maturation and decelerate turnover of CFTR (e.g. VX-809, VX-661, VX-152, VX-440, CTP-656, Miglustat, Riociguat), and (3) ‘potentiators’, which increase open channel probability and/or gating potential of apically localized CFTR (e.g. VX-770).
