Figure 7. Retinal Oximetry with vis-OCT.
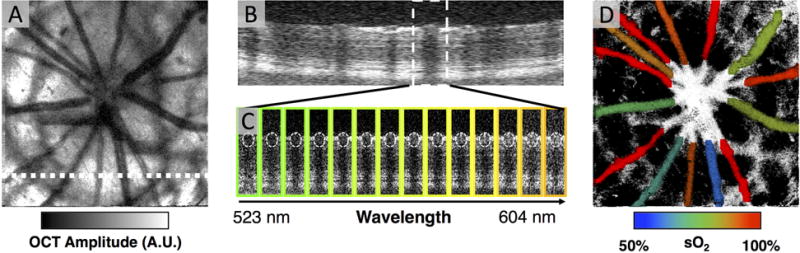
(A) An en face vis-OCT image from a healthy rat eye. A.U.: arbitrary units. (B) A full-spectrum vis-OCT B-scan from the white dashed line in (A). (C) For the vessel within the white dashed box in (B), fourteen split-spectrum B-scans were generated by ‘splitting the spectrum.’ The border around each split-spectrum B-scan represents the approximate color corresponding to the wavelengths split from the full-spectrum. The wavelengths ranged from 523 nm to 604 nm (D) After fitting the OCT signals at the bottom of white dashed circles in (C), the oxygen saturation of hemoglobin was found. The vessel in (C) had an oxygen saturation of 0.5, which indicates that it was a vein.
