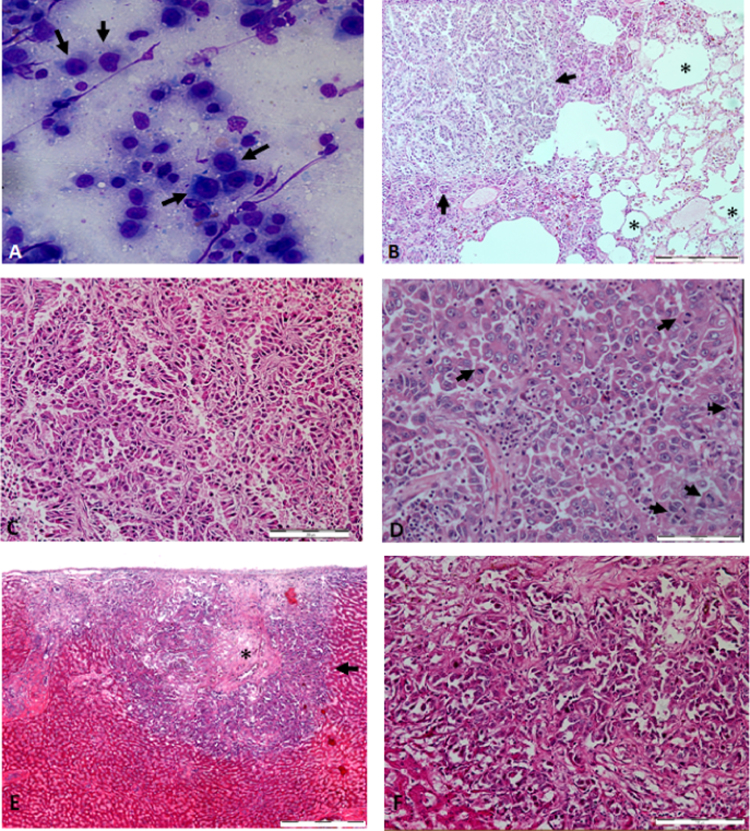
Fig. 3.
(A) Cytology of the lung smear. Arrows shows the variously sized cuboidal to polygonal cells with multiple nucleoli, large nuclei and fine vacuolated cytoplasm. (B) Histopathology section of lung (×40 magnification). There was infiltration of papillary structures to the lung tissue, leading to loss of lung structure (arrows) and identifiable alveolar structure (*). Bar, 500 µm. (C) Histopathology section of the lung (×100 magnification) shows papillary structure of the neoplasm infiltrating the lung. Bar, 200 µm. (D) Histopathology section of the lung (×200 magnification). The presence of several mitotic figures (arrows) under one hpf indicates malignancy. Bar, 100 µm. Histopathology section of the liver (×40 magnification). A liver nodule (arrow) contains a necrotic centre (*) with similar papillary structure histomorphology as found in the lung, surrounded by identifiable liver structure. Bar, 500 µm. (F) Histopathology section of the liver (×200 magnification). Similar papillary structure histomorphology was found in the lung. Bar, 100 µm.