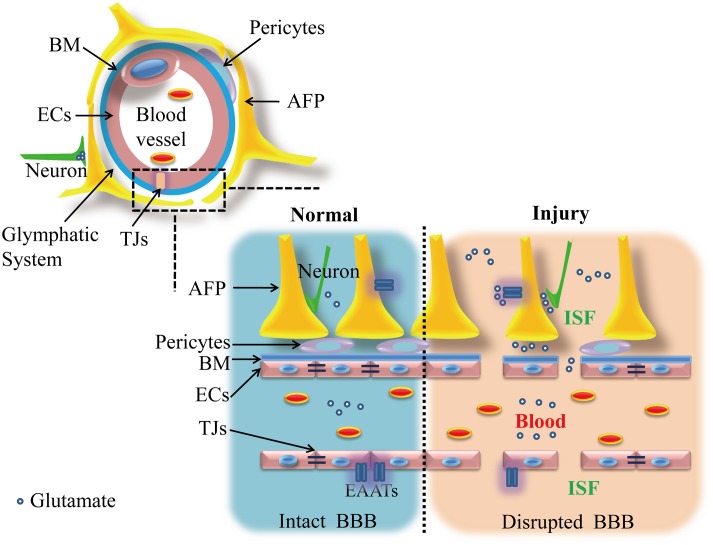
FIGURE 1.
Illustration of the components of the blood–brain barrier (BBB) and distribution of glutamate under normal and injury conditions. Under normal conditions, the structure of the BBB is intact and includes a bilayer of endothelial cells (including TJs), astrocyte end feet and pericytes in combination with a basement membrane. These layers separate glutamate into two relatively isolated circumstances: brain and blood. However, after a brain injury, the BBB is disrupted, and the levels of glutamate in blood and brain both markedly increase. This figure was modified from Liu et al. (2016) with the permission of the authors. AFPs, astrocytic feet processes; BM, basement membrane; ECs, endothelial cells; EAATs, glutamate transporters; ISF, interstitial fluid; TJs, tight junctions.