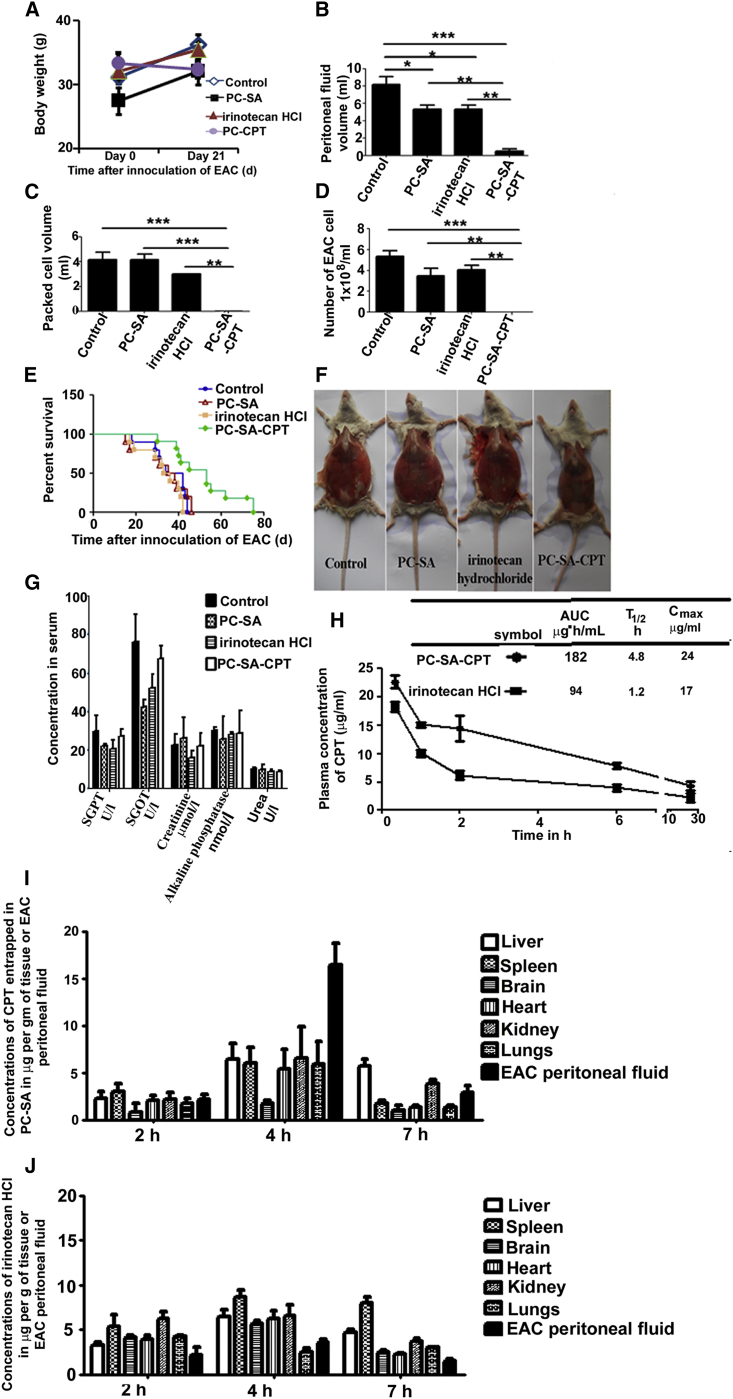
Figure 6.
PC-SA Liposomes Inhibit EAC Growth as a Single Agent and in Combination with Anticancer Drugs
22 mg of PC-SA liposomes, 20 mg/kg of irinotecan HCl (a semisynthetic derivative of CPT), and 20 mg/kg of CPT entrapped in 22 mg of PC-SA liposomes were administered on day 2 intravenously into EAC-bearing Swiss albino mice. (A) Body weights were taken. (B–D) Mice were sacrificed on day 21, and (B) peritoneal fluid volume, (C) packed cell volume, and (D) the number of EAC cells were measured. (E) The cumulative survival curve (Kaplan-Meier survival plot) of another set of mice was plotted against time after inoculation of EAC in days. (F) Images of mice. (G) No significant toxic effects of PC-SA-CPT, PC-SA, and irinotecan HCl were observed in any of the organs of normal Swiss albino mice. (H) Plasma concentration time curves of CPT (20 mg/kg) in PC-SA and irinotecan HCl (20 mg/kg) following i.v. injection in normal Swiss albino mice. Each value represents the mean ± SD (n = 3). (I and J) Mean CPT concentration-time profiles in organs and the peritoneal cavity after single intravenous administration of CPT (20 mg/kg) entrapped in 22 mg of PC-SA (I) or 20 mg/kg irinotecan HCl (J) in EAC-bearing Swiss albino mice. Data represent mean ± SE for three animals per group performed in triplicate.