FIGURE 1.
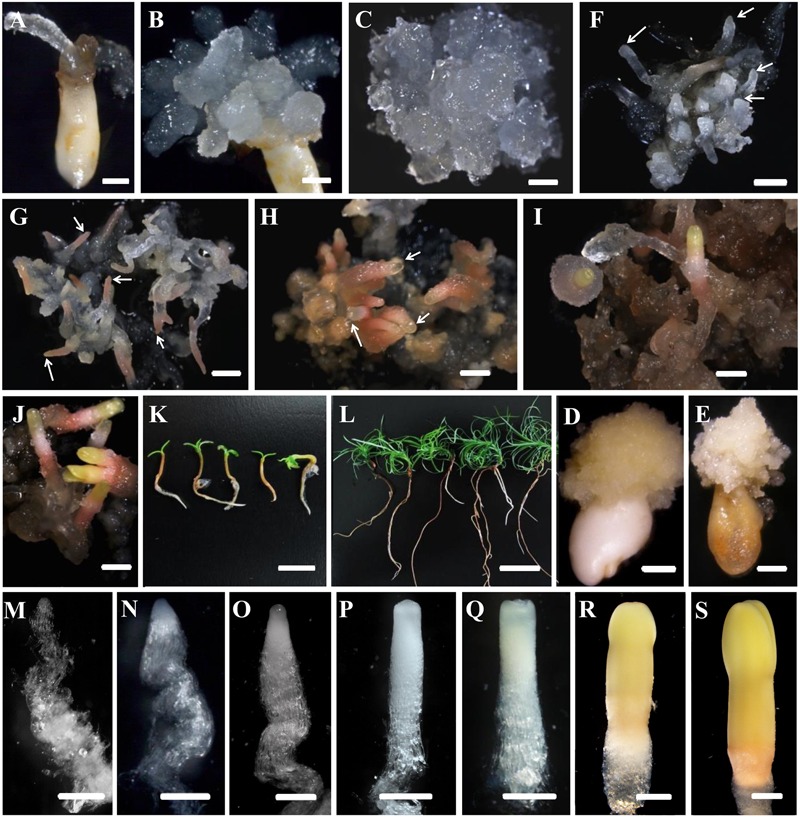
Developmental stages of SE (A–L) and zygotic embryogenesis (M–S) in Cunninghamia lanceolata (Lamb.) Hook. (A,B,D,E) Embryo sacs containing immature embryos for PEM induction: (A,B) induced embryogenic tissues; (D,E) induced non-embryogenic tissues. (E,F–K) Somatic embryo induction at diverse stages in Chinese fir: (E) maintenance of PEMs that were translucent and had pointed surface protrusions; (F) formation of proembryos (arrows); PEMs on a high osmolality medium for 1 week after suspension; end of proembryogeny; (G) shaped early reddish embryos (arrows); end of early embryogeny; (H) reddish embryos with bright yellow tops (arrows); the transition to late embryogeny; (I) early cotyledonary embryos; (J) late cotyledonary embryos; (K,L) seedlings germinated from somatic embryos at 1 week (K) and 1 month (L). (M–S) Zygotic embryo development of Chinese fir based on Pullman and Webb (1994): (M) cleaved polyembryogeny before a dominant embryo forms; (N) proembryo, the beginning of early embryogeny; the dominant embryos has formed; (O) further developed dominant embryo with embryonal mass and suspensor prototypes; ready for late embryogeny; (P) dominant embryo with a more mature embryonal mass and suspensor; (Q) embryonal mass to cotyledon formation; (R,S) maturation of cotyledonary embryo. Bars = 1 mm for (A–J); 500 μm for (M–S); 1 cm for (K,L).
