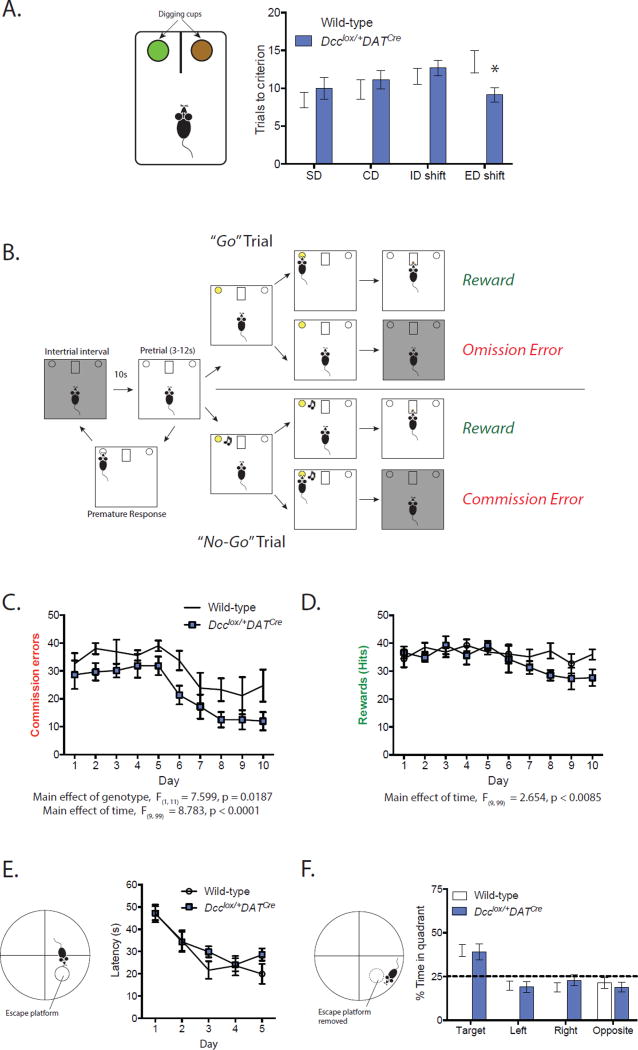
Figure 4. DCC-dependent rerouting of mesolimbic dopamine axons to the mPFC improves cognitive control.
(A) Dcclox/+DATCre mice required fewer trials than their wild-type littermates in the extradimensional (ED) part of the attentional set shifting task, indicating superior behavioral flexibility (Two-way mixed design ANOVA, genotype × task interaction, F(3, 72) = 2.749, p = 0.049; no effect of genotype, F(1, 24) = 0.01038, p = 0.9197; no effect of task, F(3, 72) = 2.123, p = 0.1048. Significant difference between genotypes during the ED shift, Bonferroni post hoc, p <0.05. Dcclox/+DATCre n = 14; Wild-type n = 12). (B) Diagram of the Go/No-Go task we adapted for mice. (C) Dcclox/+DATCre mice make significantly fewer commission errors than wild-type mice. (Two-way mixed design ANOVA, main effect of genotype, F(1, 11) = 7.599, p = 0.0187; main effect of time, F(9, 99) = 8.783, p < 0.0001; no interaction, F(9, 99) = 0.3734, p = 0.94. Dcclox/+DATCre n = 6; Wild-type n = 7). (D) There are no differences between the genotypes on the number of ‘Hits’ (Two-way mixed design ANOVA, no effect of genotype, F(1, 11) = 1.998, p = 0.185; main effect of time, F(9, 99) = 2.654, p < 0.0085; no interaction, F(9, 99) = 1.473, p = 0.1686. Dcclox/+DATCre n = 6; Wild-type n = 7). (E) No differences between genotypes in spatial learning in the Morris Water Maze. (Two-way mixed design ANOVA, main effect of day, F(4, 64) = 14.67, p < 0.0001; no effect of genotype, F(1, 16) = 1.972, p = 0.1793; no interaction, F(4, 64) = 0.7876, p = 0.5375. Dcclox/+DATCre n = 10; Wild-type n = 8). (F) No differences in the amount of time spent in the target quadrant between genotypes during the probe test in the Morris Water Maze. (Two-way mixed design ANOVA, main effect of quadrant, F(3, 48) = 12.73, p < 0.0001; no effect of genotype, F(1, 16) = 0.7938, p = 0.3862; no interaction, F(3, 48) = 0.2690, p = 0.8474. Dcclox/+DATCre n = 10; Wild-type n = 8).