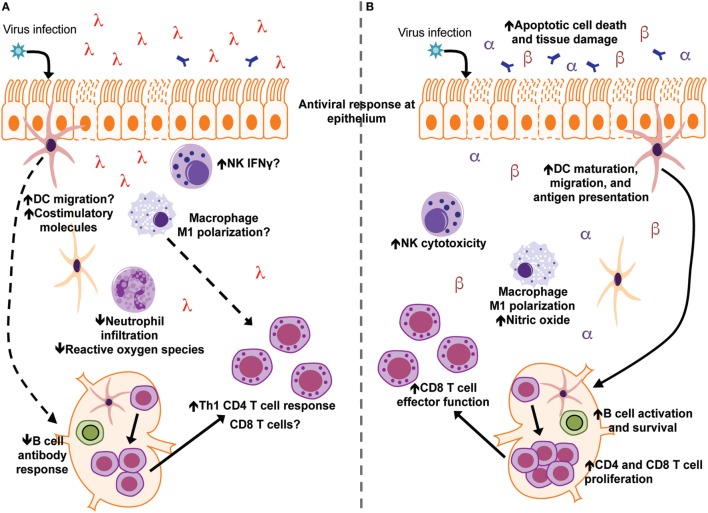
Figure 2.
Interferon lambda (IFNλ) and IFNα/β differentially modulate immune responses during acute viral infection and tissue inflammation. (A) Following viral infection/tissue inflammation, IFNλ modulates functions of dendritic cells (DCs) neutrophils, CD4 T cells, and the B-cell antibody response. IFNλ signaling may also regulate macrophage, NK cell, and CD8 T cell function during infection/tissue inflammation (B) type I IFN (IFNα and IFNβ) have been the subject of a greater number of studies and have more defined roles during virus infection and tissue inflammation. Type I IFN enhances functions of DCs, macrophages, NK cells, B cells, CD4 T cells, and CD8 T cells toward an inflammatory/antiviral state.