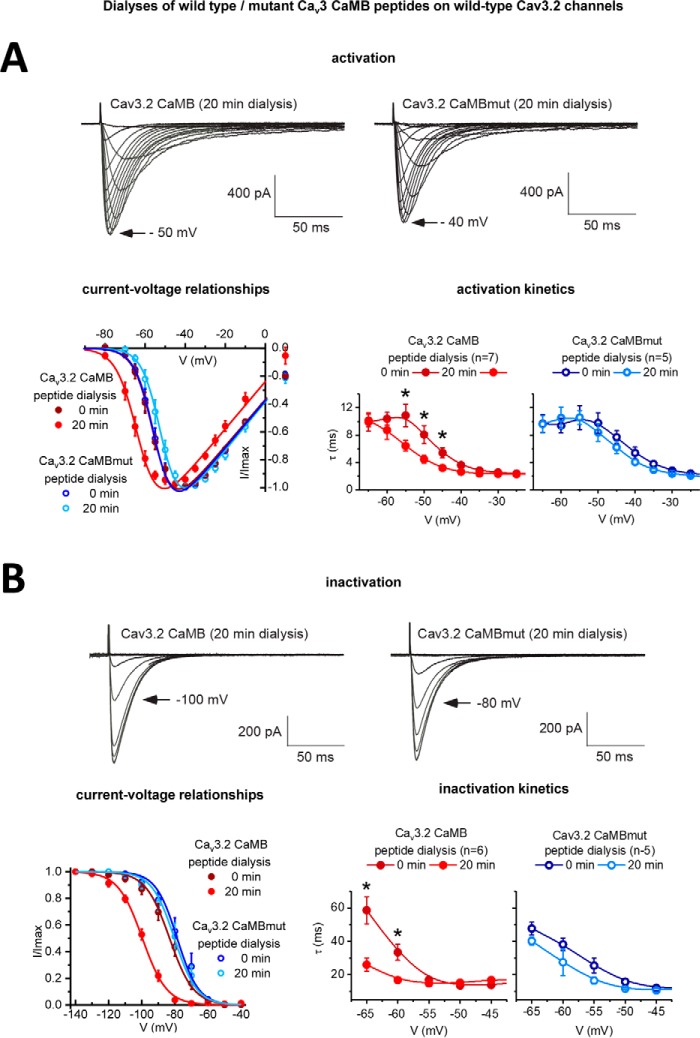
Figure 7.
Intracellular dialysis of 5 μm Cav3 CaMB peptide but not mutated (CaMBmut) peptide causes a hyperpolarization shift and faster channel kinetics in Cav3.2 channels. Transfected Cav3.2 channels in HEK-293T cells were evaluated by whole-cell patch-clamp electrophysiology for activation (A) and inactivation (B) at start of patch recording (time 0) and after 20 min of intracellular dialysis of 26-mer Cav3 CaM-binding (CaMB) peptide or mutated CaM-binding (CaMBmut) peptide (peptide sequences in Figs. 2B and 4B). Representative current traces after 20-min dialyses are shown. Calcium currents were measured for their current-voltage relationships and τ mono-exponential fits for the kinetics of activation (A) and inactivation (B). Activation and steady-state inactivation curves were created with peak currents generated from a step depolarization from −110 to −80 to −10 mV and to −30 mV from holding potentials ranging from −140 to −40 mV, respectively. Statistical significance (p < 0.05) using a non-parametric Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test for the kinetic data is shown by * measured before and after equilibration of the intracellular dialysis of Cav3 CaMB peptide or mutated CaM binding (CaMBmut) peptide. n values for current-voltage relationship Cav3 CaMB peptide (n = 7) and CaMBmut (n = 6). n values for inactivation Cav3 CaMB peptide (n = 5) and CaMBmut (n = 6).