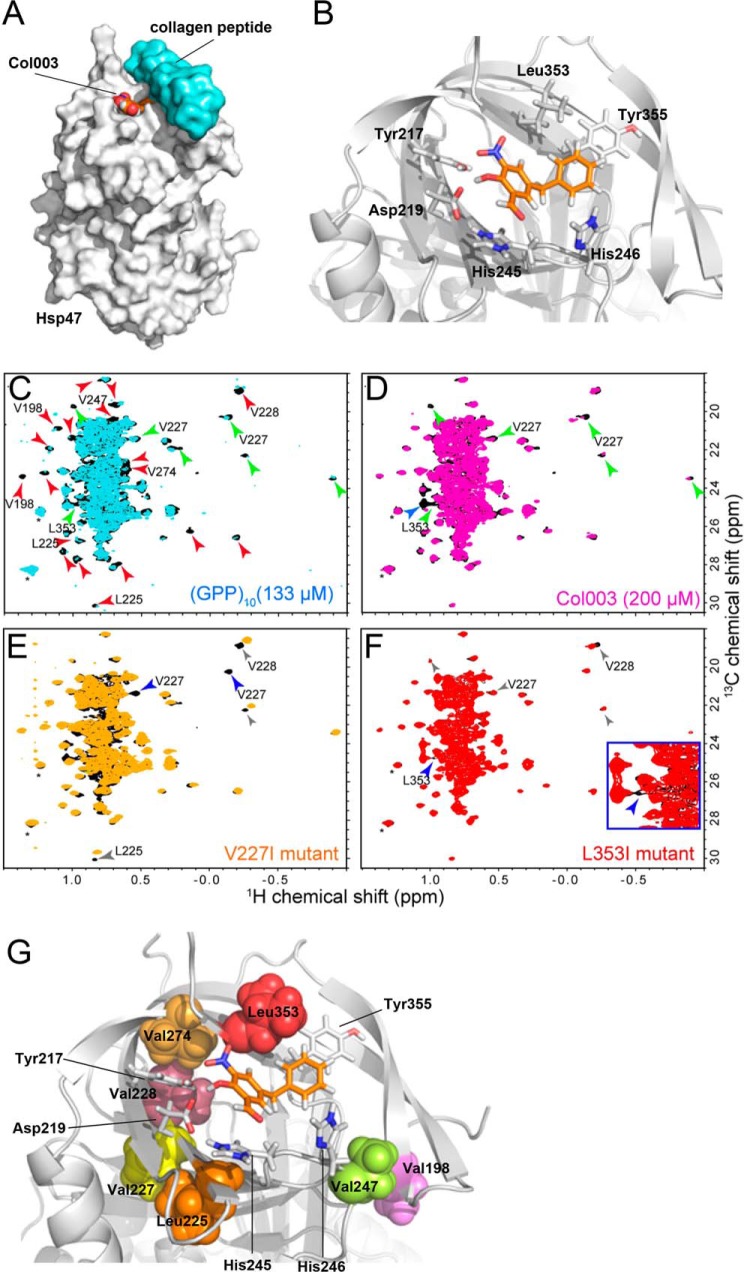
Figure 4.
Proposed model of the binding of Col003 and NMR analyses of Hsp47. A, overview of the structure of Hsp47 (gray surface model) in complex with Col003 (space-filling model with orange carbon atoms) and collagen peptide (light blue surface model). X-ray structure of Hsp47: Protein Data Bank code 4AU2. B, detailed view of the key residues of Hsp47 (stick model with gray carbon atoms) that interact with and surround Col003 (stick model with orange carbon atoms). C, comparison of the Leu/Val methyl regions of the 1H-13C HMQC spectra of Hsp47 in the presence (cyan) and absence (black) of 133 μm (GPP)10 as a trimer. D, comparison of the Leu/Val methyl regions of the 1H-13C HMQC spectra of Hsp47 in the presence (magenta) and absence (black) of 200 μm Col003. The red and blue arrowheads indicate resonances that were substantially perturbed by binding of Hsp47 to (GPP)10 and Col003, respectively. The green arrowheads indicate resonances that were commonly perturbed by the binding of Hsp47 to either substrate. The solvent peaks are indicated by asterisks. E and F, comparisons of the Leu/Val methyl regions of the 1H-13C HMQC spectra of wild-type Hsp47 (black) and Hsp47 containing a V227I (E; orange) or L353I (F; red) mutation. The resonances that disappeared upon introduction of the mutations are indicated by blue arrowheads. The signals that were affected by the mutation and by binding of (GPP)10 or Col003 are indicated by gray arrowheads. Resonances that were mutated in subsequent analyses (see supplemental Fig. S3) are annotated. G, positions of the mutated residues in the theoretical model of the Hsp47–Col003 complex. The mutated residues are indicated by surface representations. The residues that are located in close proximity to Col003 in the model are shown as stick representations. All of the residues are located within the collagen-binding interface.