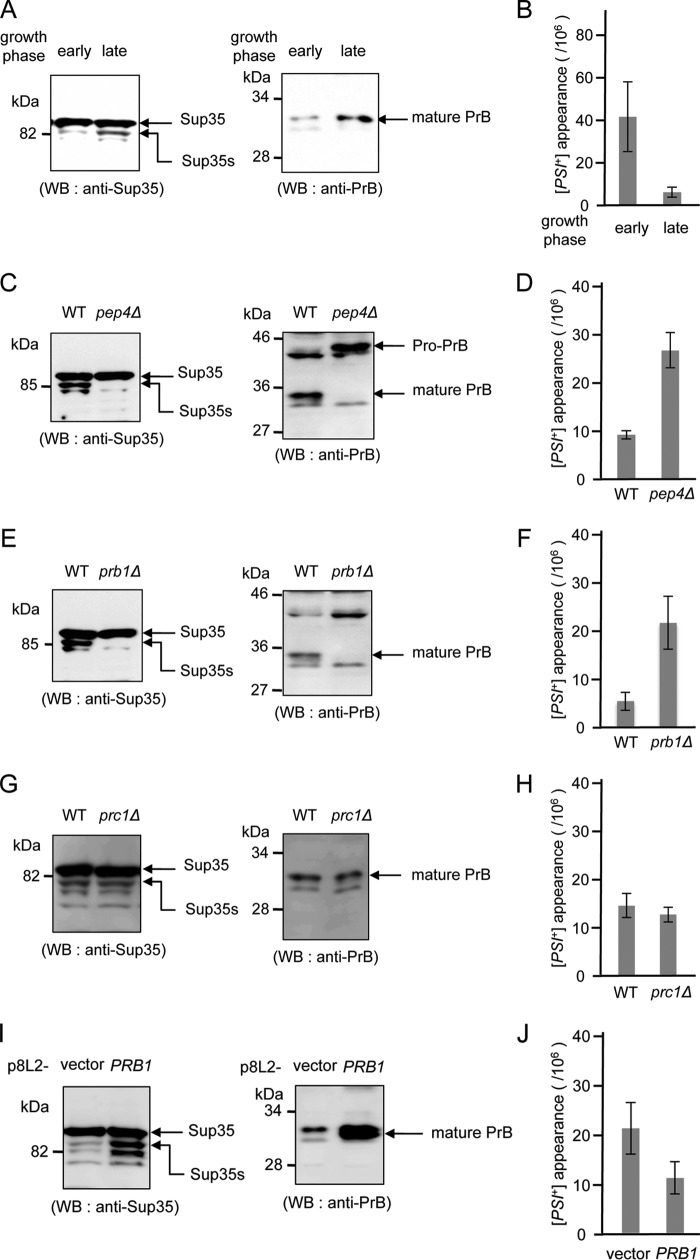
Figure 5.
The PrA–PrB proteolytic pathway negatively regulates de novo formation of [PSI+]. A, wild-type (OT60) grown in YPDA were harvested at the early log-phase or the late log-phase. Cell extracts were analyzed by Western blotting (WB) using anti-Sup35 or anti-PrB. B, cells cultured as in A were plated onto an adenine-deficient SD plates (SD-Ade). Colonies grown on the SD-Ade plates were tested for curability on YPD plates containing 2.5 mm guanidine HCl; numbers of Ade+ colonies cured by guanidine HCl were used to calculate the frequencies of spontaneous [PSI+] formation. Average results of 3 repeats are shown, bars correspond to standard deviations. C, wild-type (OT60) and pep4Δ (yAO121) grown in YPDA were harvested at the late log-phase. Cell extracts were analyzed as in A. D, the frequencies of [PSI+] formation in wild-type and pep4Δ in C were measured as in B. E, wild-type (OT60) and prb1Δ (yAO66) grown in YPDA were harvested at the late log-phase. Cell extracts were analyzed as in A. F, the frequency of the appearance of [PSI+] in wild-type or pep4Δ in E was calculated as in B. G, wild-type (OT60) and prc1Δ (yAO179) grown in YPDA were harvested at the late log-phase. Cell extracts were analyzed as in A. H, the frequency of the appearance of [PSI+] in wild-type or pep4Δ in G was calculated as in B. I, wild-type (yAO109) and p8L2-PRB1 transformants (yAO110) grown in YPDA were harvested at the early log-phase. Cell extracts were analyzed as in A. J, the frequency of the appearance of [PSI+] in wild-type or p8L2-PRB1 transformants was calculated as in B. Guanidine curability of all strains in B, D, F, H, and J is shown in supplemental Table S3. Average results of 3 repeats are shown, bars correspond to standard deviations.