Figure 1.
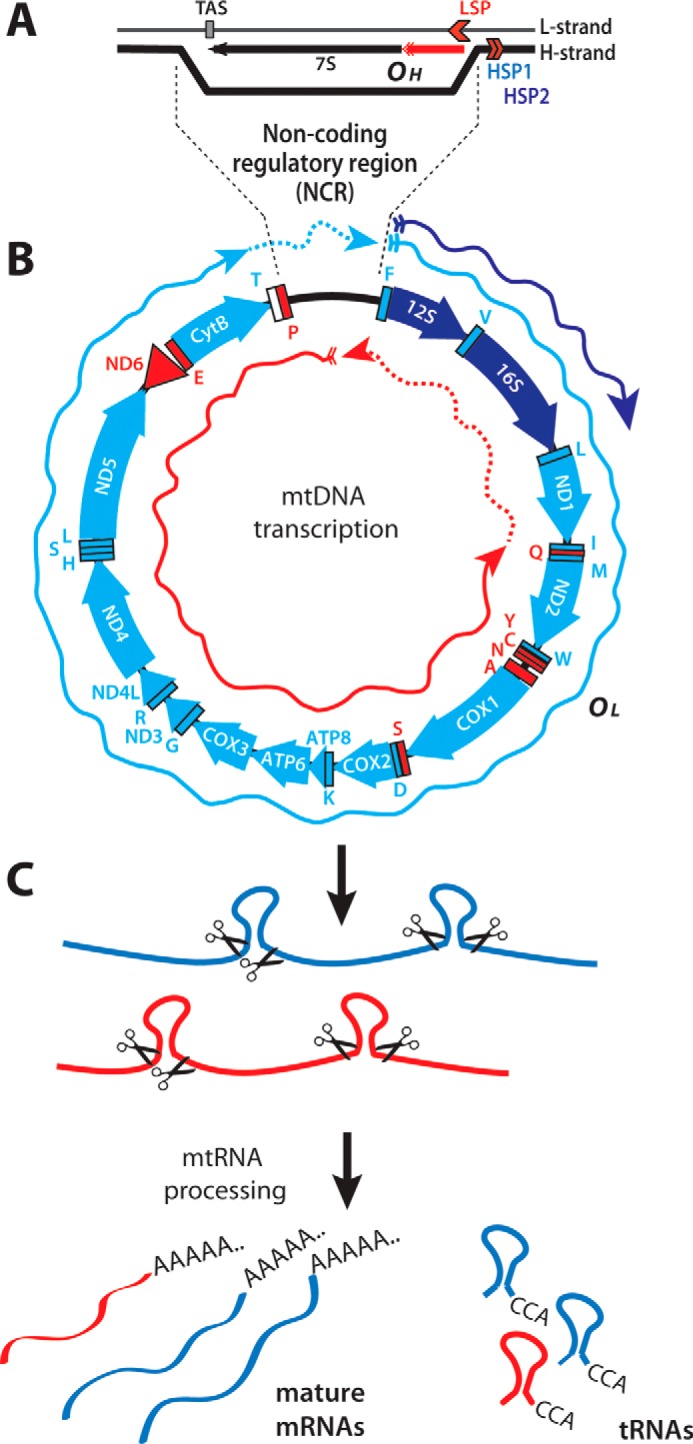
Mammalian mitochondrial genome and its transcripts. A, schematic representation of the noncoding regulatory region containing the D-loop mtDNA formed by the extended RNA primer (red) originating from the L-strand promoter (LSP). TAS, termination-associated sequence. B, the mitochondrial genes are schematized using clockwise and counterclockwise arrows, representing genes encoded by the H- and L-strands, respectively. The H-strand transcripts (rRNAs, mRNAs, and tRNAs) are represented in blue (light or dark blue for products generated from HSP2 or HSP1, respectively). tRNAs and the only mRNA (ND6) produced by L-strand transcription are sketched in red. Blue and red arrows represent the polycistronic transcripts produced by transcription initiated at the H- and L-strand promoters, respectively. C, the polycistronic RNA precursors are processed by excising the tRNAs flanking the open reading frames. Mature messenger and ribosomal RNAs are then maturated by the addition of a 3′-poly(A) tail before being translated or incorporated into mitochondrial ribosomes.
