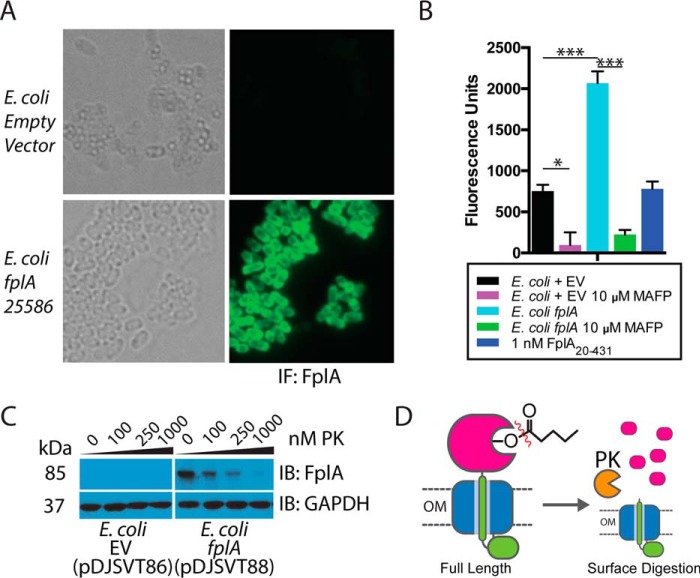
Figure 6.
Expression of full-length FplA in E. coli and functional analysis. A, an OmpA(1–27) signal sequence allows for robust expression of FplA(20–760) on the surface of E. coli as seen by fluorescence microscopy with an anti-FplA antibody. B, enzymatic activity of FplA when live E. coli is added to reactions containing 4-MuH as a fluorescent substrate. C, PK, a cell-impenetrable nonspecific protease, is able to digest surface-exposed FplA, but not the cytoplasmic protein GAPDH. D, schematic of PK cleavage of full-length FplA from the surface of E. coli. EV, empty vector. Statistical analysis was performed using a multiple-comparison analysis by one-way analysis of variance. *, p ≤ 0.05; ***, p ≤ 0.0005. Error bars, S.D. IB, immunoblotting.