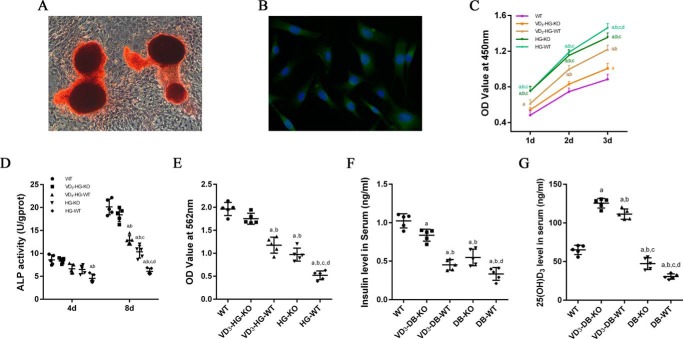
Figure 1.
1,25(OH)2D3 (VD3) decreases abnormal proliferation and promotes osteogenic differentiation of osteoblasts in high-glucose environment. A, alizarin red staining of primary osteoblasts after 21-day osteogenic induction. B, immunofluorescent staining of OCN in osteoblasts. Alizarin red-positive nodules and obvious expression of OCN proves a successful isolation and culture of primary osteoblasts. C, cell viability determined by the CCK-8 assay at 1, 2, and 3 days in different groups (n = 6 specimens/group). D, cell differentiation assessed by ALP activity at 4 (4d) and 8 days (8d) (n = 5 specimens/group). E, quantification of mineralization nodules in different groups (n = 5 specimens/group). F and G, serum insulin (F) and serum 25(OH)D3 (G) were detected by ELISA (n = 5 specimens/group). The data are presented as means ± S.D. a, p < 0.05 for WT versus others; b, p < 0.05 for VD3-HG(DB)-WT or HG(DB)-KO or HG(DB)-WT versus VD3-HG(DB)-KO; c, p < 0.05 for HG(DB)-KO or HG(DB)-WT versus VD3-HG(DB)-WT; d, for HG(DB)-WT versus HG(DB)-KO. DB represents diabetes mellitus, and HG represents high glucose.