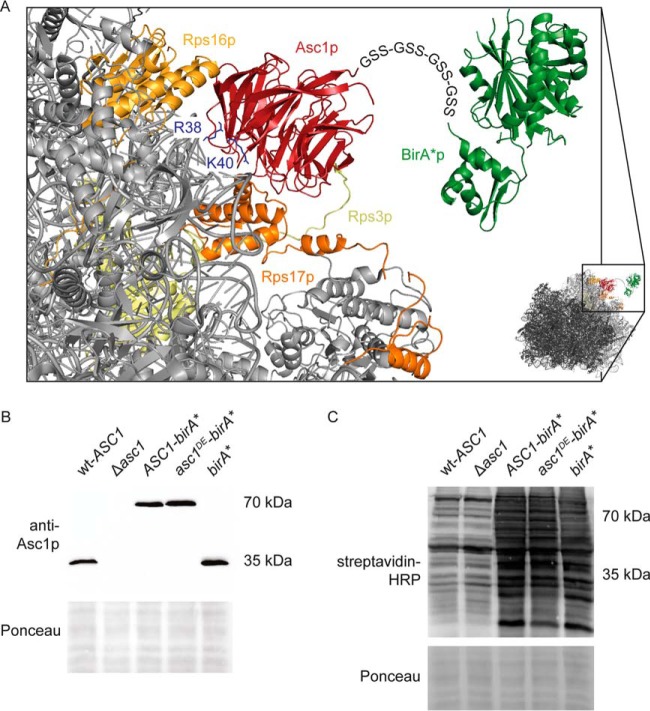
Fig. 1.
Scheme of Asc1-BirA*p at the head of the 40S ribosome. A, The Asc1 protein is a constituent of the 40S ribosomal subunit and interacts physically with the ribosomal proteins Rps3p, Rps16p and Rps17p. Amino acid residues Arg38 and Lys40 contribute to ribosome-binding and their exchange to Asp or Glu (Asc1DEp) weakens ribosome-binding. The BirA* protein is fused to the C-terminus of Asc1p and Asc1DEp via four repeats of a Gly-Ser-Ser linker sequence indicated as letter sequence. Because of the ribosome averted orientation of the Asc1p C-terminus, ribosome binding of the fusion proteins should not be sterically compromised. The crystal structure data of the S. cerevisiae 80S ribosome and the E. coli BirA protein derive from the PDB entries 4V88 (10) and 1BIB (73) and were combined to model the fusion protein with the PyMOL Molecular Graphics System software. B, Expression of the Asc1-BirA* and the Asc1DE-BirA* fusion proteins (∼70 kDa) from a high copy number plasmid in the Δasc1 strain background provides wild-type-like Asc1p levels. Proteins were detected in Western experiments using an Asc1p-specific antibody. The Ponceau staining of the lane is shown for a small part of the lanes. C, Protein biotinylation, detected with horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-coupled streptavidin, was elevated in strains expressing Asc1-BirA*p, Asc1DE-BirA*p or the mere BirA* protein cultivated in the presence of biotin. Parts of the Ponceau stained lanes are shown.