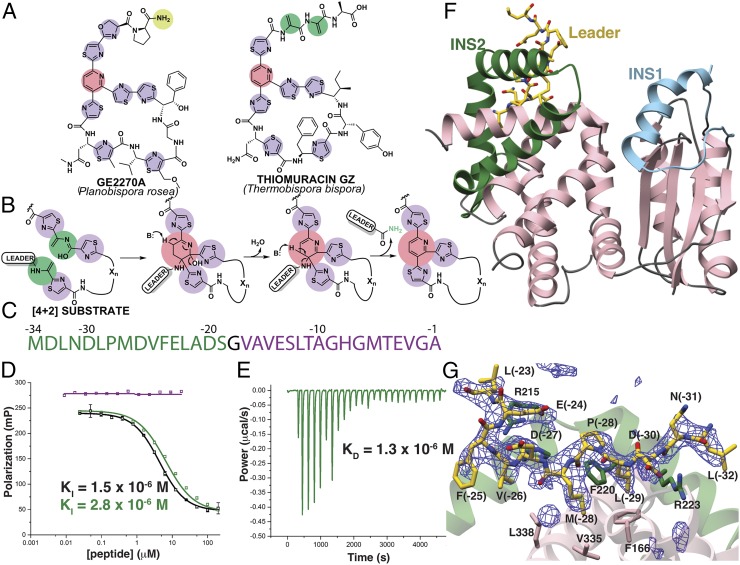
Fig. 1.
Scheme of enzyme-catalyzed pyridine formation and leader peptide binding of the pyridine synthase, TbtD. (A) Chemical structures of representative thiopeptides with residues color-coded by posttranslational modification. (B) Proposed enzymatic route for the installation of the central nitrogenous six-membered ring from two dehydroalanine residues, followed by the elimination of water and the leader peptide. (C) Primary sequence and numbering scheme of the TbtA leader peptide with the fragment that is engaged by TbtD colored in green. (D) Competition fluorescence polarization binding experiments where TbtD saturated with fluorescently labeled full-length leader peptide is challenged with either unlabeled full-length leader peptide (black curves), or fragments corresponding to the N-terminal (green curve and sequence) or C-terminal (purple curve and sequence) regions of the leader peptide. The N-terminal fragment is sufficient to compete with avidity similar to that of the full-length leader peptide. (E) ITC shows that the N-terminal leader peptide fragment binds to TbtD. (F) Overall structure of TbtD in complex with the N-terminal leader fragment, showing insertions 1 (cyan) and 2 (green) that distinguish the [4+2] enzymes from the LanB elimination domains. (G) Simulated annealing difference Fourier map (Fobs – Fcalc) contoured at 2.5σ showing residues from the leader peptide that bind to a region near insertion 2 (green) in TbtD.