Figure 5.
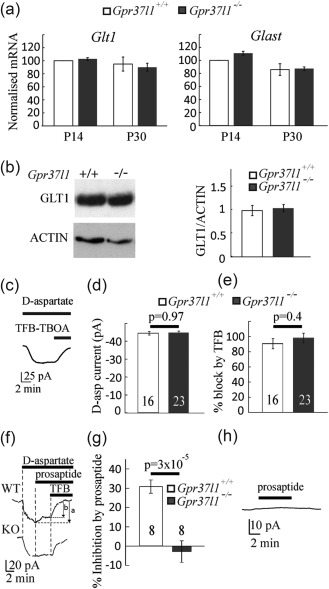
Assessment of glutamate uptake in astrocytes. (a) Expression of mRNA for the glutamate transporters Glast and Glt‐1 assessed by RT‐PCR in hippocampus from P14 and P30 Gpr37l1 +/+ and Gpr37l1 –/– mice. Data are mean ± s.e.m from four experiments. (B) Expression of GLT‐1 analyzed by Western blot in hippocampus from P14 Gpr37l1 +/+ and Gpr37l1 –/– mice (quantified relative to actin). Data are mean ± s.e.m of four experiments. (c–e) Glutamate uptake current in astrocytes (number of cells on bars). (c) Example of a d‐aspartate (200 µM)‐evoked current in an astrocyte at −100 mV, and its inhibition by TFB‐TBOA (10 µM). (d) Current magnitude. (e) Percentage inhibition of the current by TFB‐TBOA. (f–h) Activation of GPR37L1 inhibits glutamate transport in astrocytes. (f) The d‐aspartate (200 µM)‐evoked inward current is partly inhibited by prosaptide (10 µM, see the difference between the arrows marked a and b in the Gpr37l1 +/+ cell but not in the Gpr37l1 –/– cell). (g) Quantification of the inhibition of the d‐aspartate evoked current by prosaptide. (h) Prosaptide does not evoke a current in the absence of d‐aspartate (in the WT)
