Figure 1. Vorinostat synergizes with AZD1775 to inhibit in vitro clonogenic survival of HNSCC cells expressing high-risk mutp53.
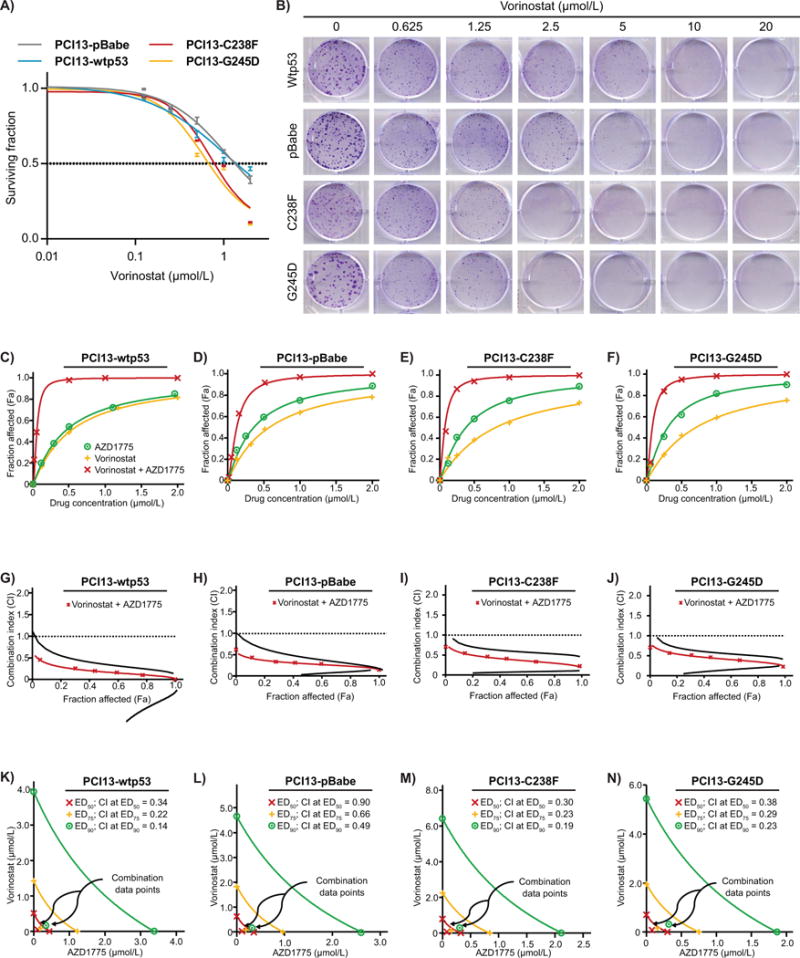
A, clonogenic survival curves for isogenic HNSCC PCI-13 cells lacking p53 (pBabe null), expressing wtp53 or high-risk mutp53 (C238F, G245D) and treated for 48 hours with a range of vorinostat concentrations (0.01-20 μmol/L) to determine the IC50. B, representative images of the results of clonogenic survival assays. C-F, assessment of the degree of synergy between vorinostat and AZD1775 in PCI13-Wtp53, PCI13-pBabe, PCI13-C238F, and PCI13-G245D, using the Chou and Talalay method (median dose-effect analysis). Vorinostat and AZD1775 were used at constant ratios (1:1 and 2:1 respectively). G-J, Fa-CI plots generated to determine the CI values (< 1.0 indicate synergism). The CI values for combination of effective drug doses (ED) that result in clonogenic survival inhibition of 50% (ED50; fa = 0.5), 75% (ED75; fa = 0.75), and 90% (ED90; fa = 0.90) were generated from the conservative isobolograms. The ED50 (red X), ED75 (green crosses) and ED90 (blue circles) graphed against fractional concentrations of vorinostat and AZD1775 on the y and x axis, respectively are indicated. K-N, conservative isobologram plots demonstrate that vorinostat and AZD1775 acts synergistically to inhibit in vitro clonogenic survival of HNSCC cells. All treatments were performed in triplicate and each experiment was repeated at least three times.
