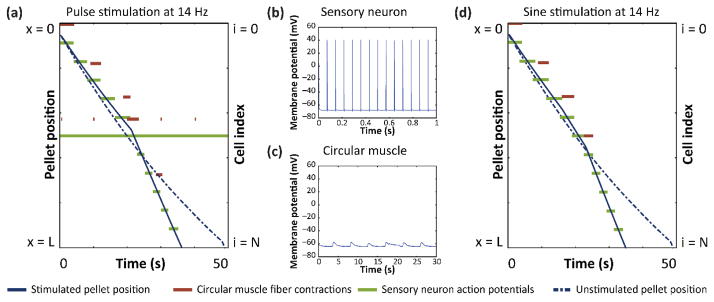
Figure 2. Electrical stimulation reduces transit time.
(a) Pellet position, circular muscle activity, and sensory neuron activity over time during 14 Hz, 200 μs pulse stimulation at 1 mA. (b) Sensory neuron action potentials during pulse stimulation in (a). (c) Circular muscle subthreshold oscillations during pulse stimulation in (a). (d) Pellet position, circular muscle activity, and sensory neuron activity over time during 14 Hz sine stimulation at 1 mA.