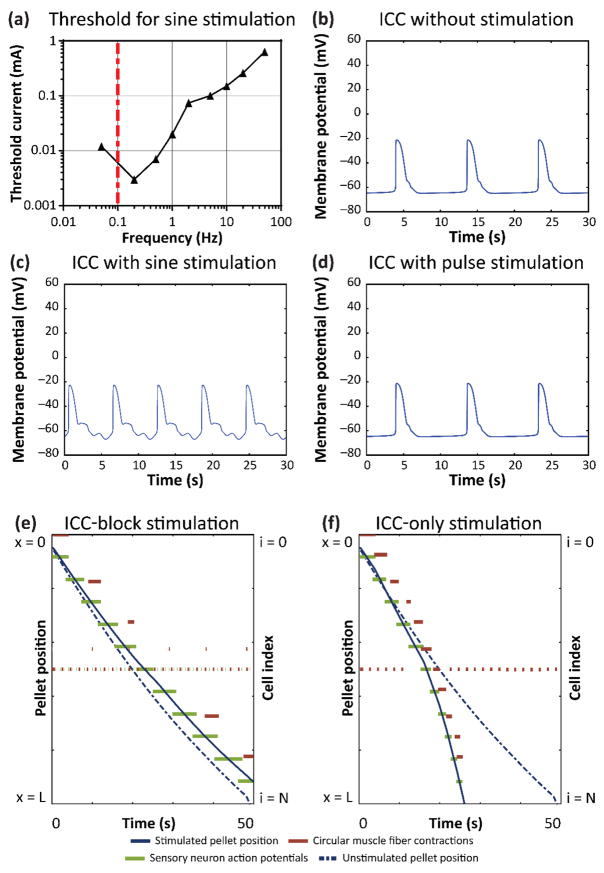
Figure 4. Role of ICC in electrical stimulation of gut motility.
(a) Threshold current required to entrain ICC pacemaker frequency to match sine stimulation frequency. Transmembrane potential of the ICC at position L/4 in the model of motility during (b) no stimulation, (c) 0.5 Hz sine wave stimulation, and (d) 0.5 Hz, 200 μs pulse stimulation at 1 mA. Pellet position, circular muscle activity, and sensory neuron activity during 0.5 Hz, 1 mA sine wave stimulation with electrical stimulation (e) influencing enteric neurons and smooth muscle, but not ICC, and (f) influencing only ICC, but not enteric neurons and smooth muscle.