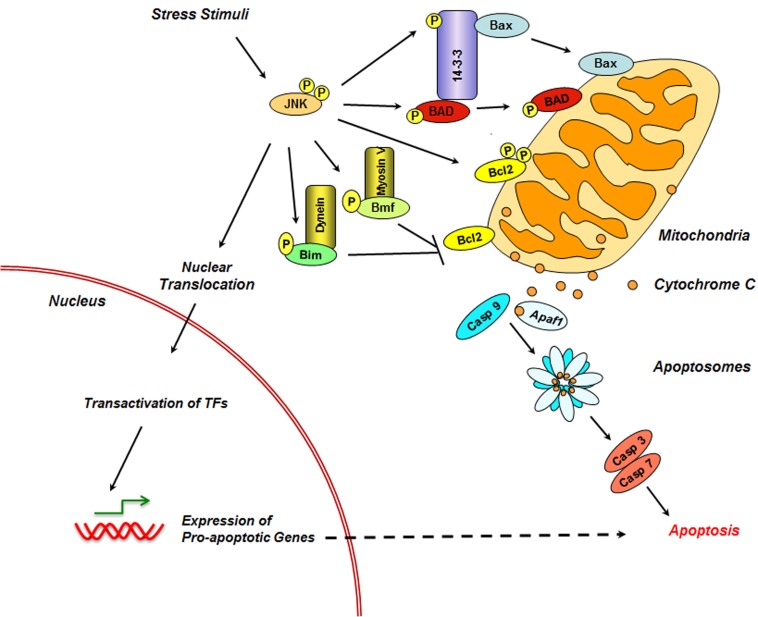
Figure 1. Role of JNK in Intrinsic Apoptosis.
JNK promotes intrinsic apoptosis by multiple mechanisms. In one mechanism, JNK stimulates the expression of apoptosis-specific genes through the transactivation of c-Jun and other target transcription factors (TF). In addition, JNK phosphorylates Bim and Bmf from their scaffold proteins to inhibit the anti-apoptotic activity of Bcl2. JNK also inhibit the activity of BCL2 through direct phosphorylation. JNK also promotes the translocation of Bad and Bax from their 14-3-3 mediated sequestering complex through direct phosphorylation. Translocated Bax and Bad stimulate the release cytochrome C (Cyt C) from the mitochondrial inner membrane. Released cytochrome C, in combination with Apaf-1 and caspase-9 form the apoptosomes, which triggers capase-9 cascade leading to the activation of the executor caspases, caspase-3 and -7 and apoptosis.