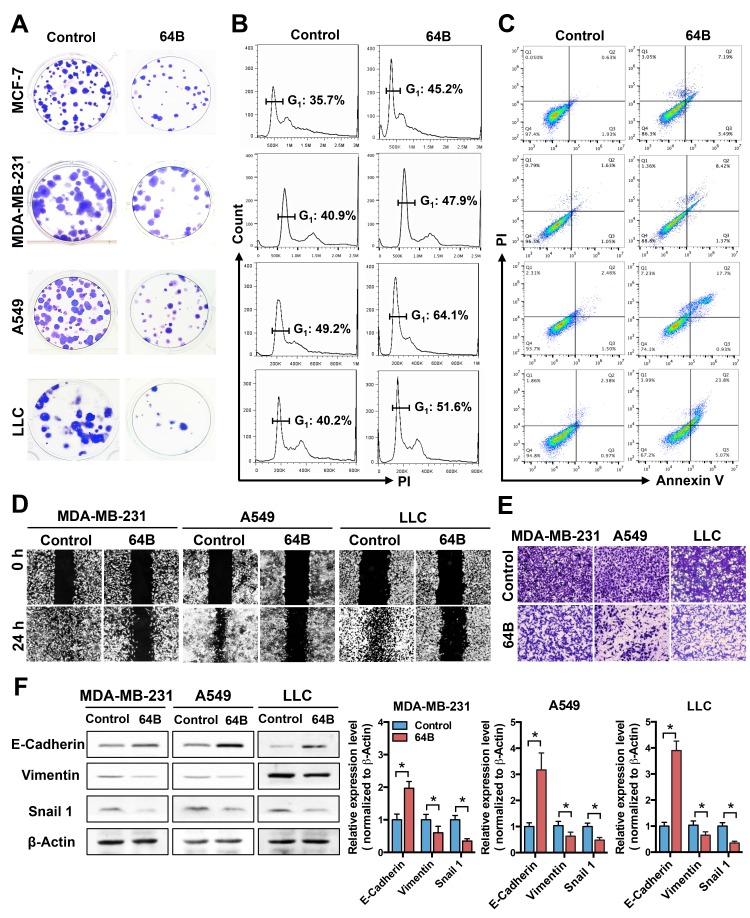
Figure 1. 64B exerts potent cytotoxicity in tumor cells and impairs their motility.
MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, A549 and LLC cells were pre-treated with 64B (5 μM) for 24 h prior to starting the assays below. A, 64B reduces colony formation of tumor cells. Colonies were visualized by crystal violet staining following 14-day incubation. B, 64B causes G1 arrest in tumor cells. Cells were stained with propidium iodide (PI) and the DNA content was analyzed by flow cytometry, the cell cycle distribution was quantified by FlowJo software. C, 64B induces apoptosis in tumor cells. Following dual staining with Annexin V-FITC and PI, cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. D, 64B impedes tumor cell migration. Scratch wounds were generated in cell monolayer and the amount of gap closure measured following 24-h incubation. E, 64B diminishes tumor cell invasion. Cells were seeded in matrigel-coated transwell chambers and incubated for 24 h, and the invading cells on the bottom of the chamber inserts were stained with crystal violet. F, Western blot analysis showing the protein levels of E-cadherin, vimentin, and Snail1 in 64B-treated tumor cells. Protein band intensities were quantified by densitometric analysis using ImageJ software. All data show representative results obtained from three independent experiments, and the results are reported as the mean ± SD (n = 3). *, p < 0.05.