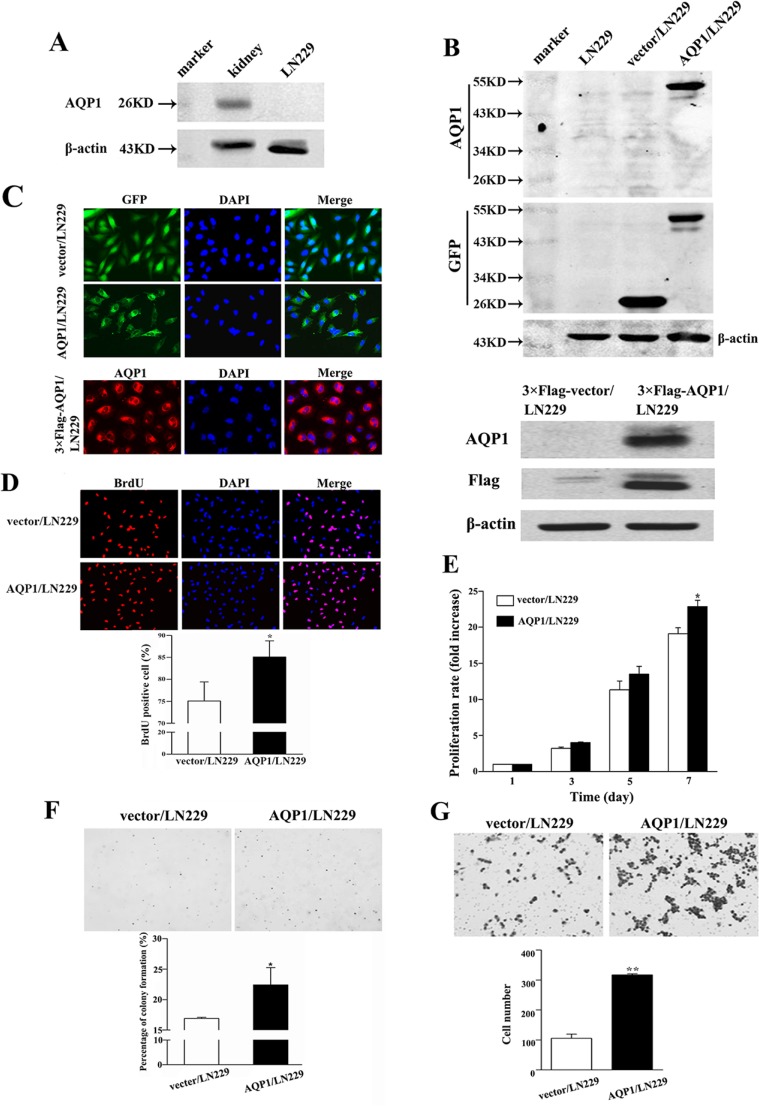
Figure 3. Overexpression of AQP1 promoted proliferation and invasion abilities of LN229 cells.
(A) In parental LN229 cells, AQP1 expression was too low to be detected by western blot. Mouse kidney tissue was used as a positive control. (B) Establishment of stable AQP1-overexpressing cells through lentiviral transfection of GFP labeled AQP1-expressing vector (upper part) and 3×Flag labeled AQP1-expressing vector (lower part). (C) Exogenous AQP1 expression was observed in AQP1/LN229 (upper part) and 3×Flag-AQP1/LN229 cells (lower part) by GFP fluorescence or anti-AQP1 antibody, respectively (200×). (D) Proliferation ability was detected by BrdU incorporation analysis in AQP1/LN229 and control cells (200×). (E) Proliferation assay was performed by MTT assays in AQP1/LN229 and control cells. (F) Colony-forming ability was examined in AQP1/LN229 and control cells (200×). (G) Invasion assays were performed in AQP1/LN229 and control cells (200×). All experiments were performed 3 times independently (Student’s t-test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01).