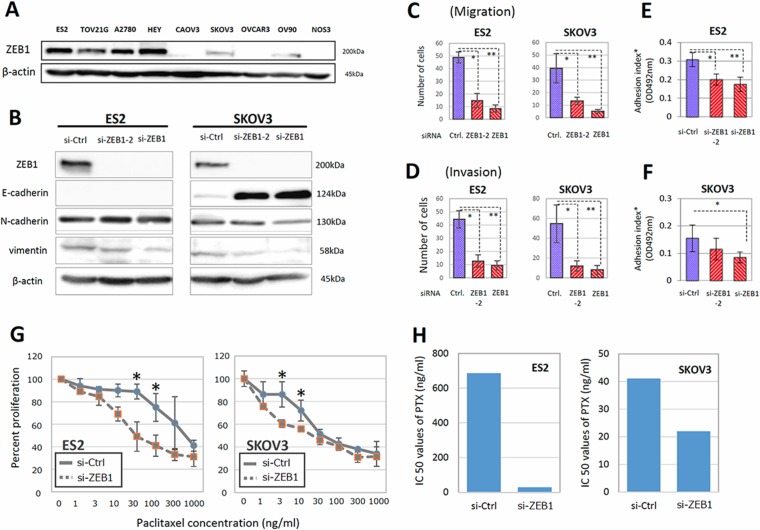
Figure 2. ZEB1 was involved in the migration, invasion, adhesion to mesothelial cells, and PTX sensitivity of EOC cells.
(A) The expression of ZEB1 in various EOC cells. ZEB1 was highly expressed in ES-2, TOV21G, A2780, and HEY cells. (B) Depletion of ZEB1 in ES-2 and SKOV3 cells and influence on expression of E-cadherin as an epithelial marker, and vimentin and N-cadherin as mesenchymal markers. (C, D) Effect of ZEB1 silencing on the migratory ability (C) and invasive potential (D) of ES-2 and SKOV3 cells. Asterisks show significance (P < 0.05). (E, F) Effect of ZEB1 silencing on the attachment of EOC cells to the confluent monolayer of human peritoneal mesothelial cells (HPMCs) (E) ES2 cells, (F) SKOV3 cells). Asterisks show significance (P < 0.05). (G, H) Restoration of PTX-resistance in ES-2 and SKOV3 cells by ZEB1 silencing. The PTX-sensitivity assay using evaluated by the MTT assay (G). Asterisks show significance (P < 0.05). ZEB1 knockdown clearly increased the sensitivities to PTX. IC50 values of PTX were significantly reduced by ZEB1 depletion in ES-2 and SKOV3 cells (H).