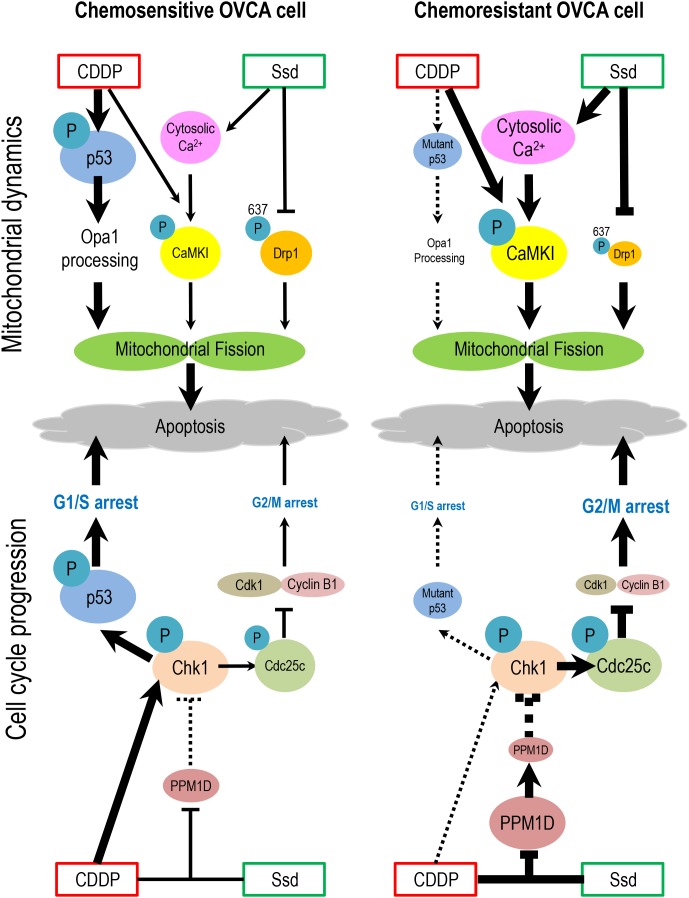
Figure 7. Hypothetical model illustrating the sensitization of chemoresistant OVCA cells by Ssd.
In chemosensitive cells, CDDP treatment results in the phosphorylation and activation of p53 and activation of Oma1, leading to Opa1 processing, mitochondrial fission and apoptosis. CDDP also activates Chk1, which phosphorylates p53, leading to G1/S arrest and apoptosis. In chemoresistant cells which often exhibit high incidence of p53 mutation and increased PPM1D stability, which inhibits Chk1 activity, CDDP fails to induce G1/S arrest and Opa1 processing. However, Ssd suppresses phospho-Ser637-Drp1 content, increases [Ca2+]c and, in the presence of CDDP, decreases MMP and increases CaMKI phosphorylation. These actions of Ssd lead to mitochondrial fission and subsequent apoptosis. Moreover, in the presence of CDDP, Ssd decreases PPM1D level, activates Chk1 and increases phospho-Cdc25c content, resulting in G2/M arrest and apoptosis.