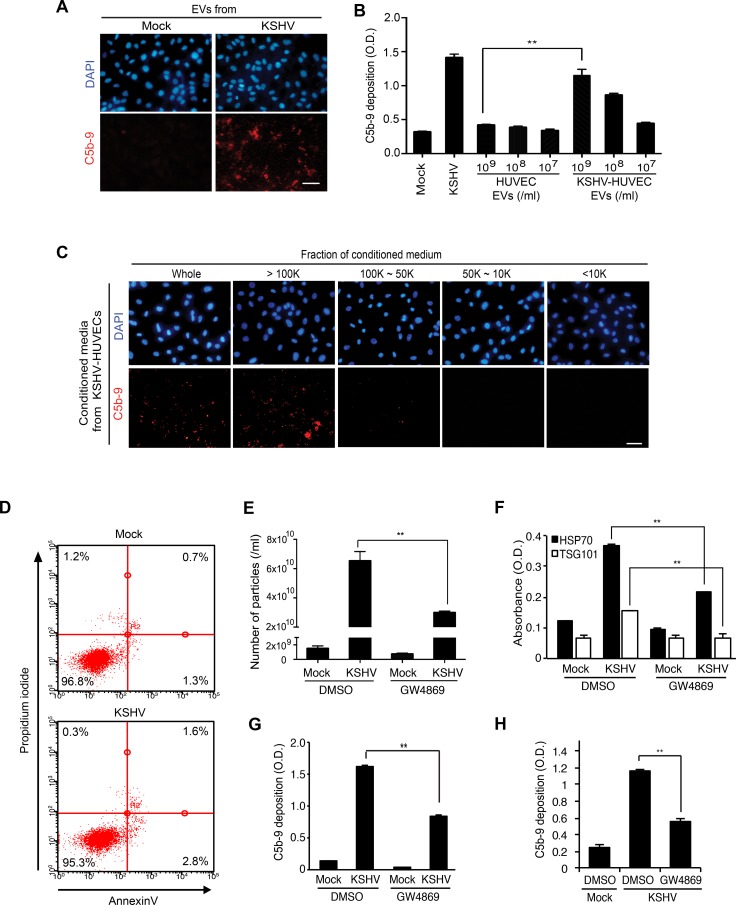
Figure 5. EVs from KSHV-infected human endothelial cells activate the complement system.
(A) EVs from KSHV-infected HUVECs activate the complement system. HUVECs treated with EVs from mock- or KSHV-infected HUVECs were examined for C5b-9 depositions. EVs isolated from the supernatant of mock- or KSHV-infected cells at 24 hpi were used to treat naive HUVECs for 24 h. After exposure to the EVs, all cells were treated with normal human serum (NHS) for another 30 min, and C5b-9 was analyzed by IFA. Scale bar: 50 μm. (B) Quantification of C5b-9 depositions on HUVECs treated with a same number of EVs from mock- or KSHV-infected HUVECs using a cell-based ELISA. Mock: mock-infected HUVECs, KSHV: KSHV-infected HUVECs. Results are shown as mean ± SD, N = 3, **p < 0.01. (C) The high molecular weight fraction of supernatant from KSHV-infected cells induces complement activation. The supernatants were fractionated using Vivaspin 20 protein concentrator spin columns with molecular weight cut-offs of 100, 50, and 10 kDa. Each isolated fraction was used to treat uninfected HUVECs for 24 h, followed by treatment with NHS. C5b-9 depositions were analyzed by IFA. Scale bar: 50 μm. (D) EVs do not induce apoptosis and cell death. HUVECs treated with the EVs from mock- or KSHV-infected human endothelial cells were examined for apoptosis and dead cells by flow cytometry analysis following staining for Annexin V- and propidium iodide (PI)-positive cells. (E–H) Inhibition of EV biogenesis during de novo KSHV infection suppressed complement activation. HUVECs pretreated with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or 10 μM GW4869 for 1 h were either mock-infected (M) or infected with KSHV (K) in the presence of the respective agents. The supernatant (CM) was collected at 24 hpi and the inhibitory effect of GW4869 on the production of EVs was analyzed by counting microparticles number and examining the levels of HSP70 in the CM using nanoparticle tracking analyzer (E) and ELISA (F), respectively. Each CM was applied to naïve HUVECs for 24 h, followed by treating with NHS for 30 min. C5b-9 depositions were analyzed by cell-based ELISA (G) and IFA (Supplementary Figure 3A) (H) Suppression of complement activation in de novo KSHV-infected HUVECs by GW4869. HUVECs pretreated with GW4869 were infected by KSHV followed by exposing the cells with NHS. The depositions of C5b-9 were quantified by cell-based ELISA. Results are shown as mean ± SD, N = 3, **p < 0.01.