Figure 2. Derivation and characterization of motoneuron.
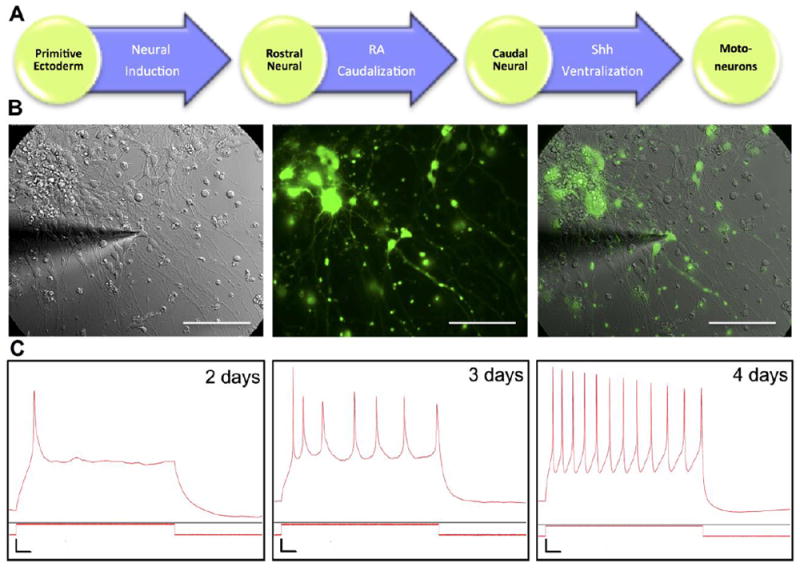
(A) Motoneurons were derived from ES cell line (HBG3) with GFP under HB9 promoter. Differentiation process started from neural induction of primitive ectoderm into rostral neural cells. Retinoic acid (RA) subsequently induced caudal neural fate, followed by Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling, converting cells to motoneurons. (B) Overlay of brightfield and fluorescence images of GFP+ motoneuron and astrocyte coculture during whole-cell current clamp experiment. Scale bar: 100 μm. (C) Representative traces of action potential (AP) measurements of motoneurons after a few days in culture. Weak single AP was observed on day 2. A weak train of APs was observed on day 3 and motoneurons were functionally mature on day 4 as evidenced by a robust firing of APs. Vertical scale bar: Vm = 10 mV, Im = 200 pA. Horizontal scale bar: 0.1 seconds.
