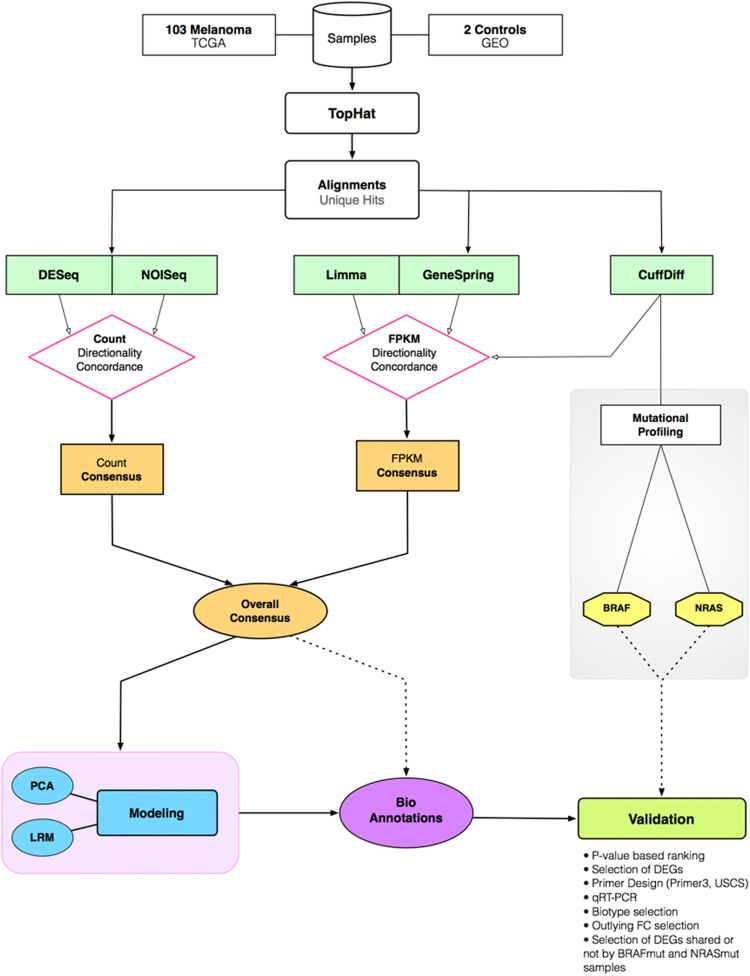
Figure 2.
RNA-Seq flowchart. The samples were processed according to the five different methods that were selected, and whose quantifications included both read counts (simply the number of reads overlapping a given feature such as a gene) and fpkm (Fragments Per Kilobase of exon per Million reads). With the latter it is possible to compare genes of different lengths, and ‘per million reads’ means that a value normalized against the library size is obtained. The consensus occurred between significant detections in both read counts and fpkm scenarios, before reaching a global result (overall consensus). The mutational profile at the right side was implemented under simplified algorithmic conditions (CuffDiff), and for two major mutations (BRAF, NRAS) (Supplementary Tables 10.1-5). The validations refer to candidates coming from all the considered scenarios.